UV absorbers (Figure 5.20) are organic compounds that absorb harmful UV light and dissipate the absorbed energy as harmless thermal energy. Important classes of UV absorbers are 2-hydro — xybenzophenones, benzotriazoles, hydroxyphenyl-s-triazines, and oxalanilides. Some other compounds such as hydroxyphenylpyrimi — dines, salicylic acid derivatives and cyano acrylates are also useful.
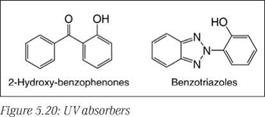 The key to effectiveness of these compounds is intramolecular hydrogen bonding and their tautomeric characteristics upon absorption of UV radiation. UV absorbers should have good solubility, compatibility with the binder and thermal stability. They should selectively absorb U V light in competition with the binder to protect it from degradation. Their protective effect increases with an increase in their concentration, inherent absorption and film thickness.
The key to effectiveness of these compounds is intramolecular hydrogen bonding and their tautomeric characteristics upon absorption of UV radiation. UV absorbers should have good solubility, compatibility with the binder and thermal stability. They should selectively absorb U V light in competition with the binder to protect it from degradation. Their protective effect increases with an increase in their concentration, inherent absorption and film thickness.
Thus, they pro-
tect the substrate and deeper layers of coating, but as such, there is no protection at the surface of the coating.
 21 января, 2016
21 января, 2016  Pokraskin
Pokraskin  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 