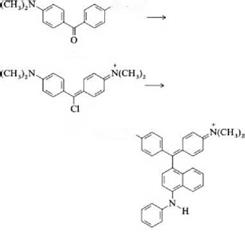
Condensation Reactions. Many triaminotriarylmethane dyes can be produced by condensation of Michler’s ketone (9) with aromatic amines. The ketone must generally be activated with phosgene or phosphorus oxychloride, whereby a reactive blue chloro compound (10) is formed from the intermediate geminal dichloride. With N-phenyl-1-naphthylamine, for example, (13) reacts to form Victoria blue B (11).
 N(CH3)2
N(CH3)2
10
11
Condensation of Michler’s hydrol (12) with 3-dimethylaminobenzoic acid (13) gives leuco crystal violet carboxylic acid (14), which is then oxidized to crystal violet lactone.
|
14 |
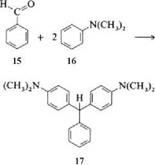
A leuco compound is also obtained when a benzaldehyde derivative is treated with 2 molar equivalents of an aniline derivative. Leuco malachite green (17) is thus formed from benzaldehyde (15) and dimethylaniline (16).
 |
With benzaldehyde-2-sulfonic and benzaldehyde-2,4-disulfonic acids, important acid dyes are synthesized by this reaction. They are known as patent blue dyes.
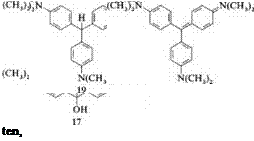 |
Crystal violet (20) can be produced directly from formaldehyde and dimethyl — aniline. The methane base (18), N, N,N’,N-tetramethyl-4,4′-methylenedianiline, is formed initially. This is then oxidized to Michler’s hydrol (12), which condenses with another molecule of dimethylaniline to give leuco crystal violet (19). The latter is converted to the dye in a second oxidation step. Pararosaniline, methyl violet, and Victoria blue can also be obtained by this reaction sequence.
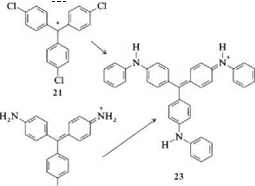 |
Nucleophilic substitution of chlorine, sulfonic acid, or amino groups by aromatic amines is a common process for producing triaminotriarylmethane dyes. Spirit blue (23) can be formed from the trichlorotriphenylmethyl cation (21) [6,7] and from pararosaniline (22) [8,9] by reaction with aniline.
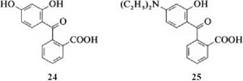 |
Synthesis of Xanthene Dyes. Phthalic anhydride reacts with 3-diethylaminophe — nol in the molten state to give rhodamine B, and with resorcinol to give fluorescein. For unsymmetrical xanthene dyes, dihydroxybenzoyl — (24) or an aminohy — droxybenzoylbenzoic acid (25) is required.
These compounds can condense and cyclize with resorcinol or substituted 3- aminophenols. Nucleophilic substitution of chlorine by amines leads to xanthene dyes which contain a sulfonic acid group [10] or hydrogen [11] instead of the carboxyl group.
 29 августа, 2015
29 августа, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 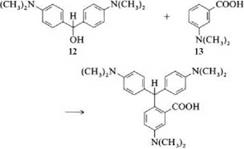
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 