Typical metal primer formulations are given below:
|
FORMULATION 7-19
|
|
pH |
9.2 |
|
nvc |
48% |
|
SG |
2.53 |
The millbase is high speed dispersed to Hegman 7 and then let down. Rhoplex WL-91, from Rohm and Haas, is a hard polymer of 41.5%nvc with a MFFT of 52°C. It requires plasticisers and coalescents for good film formation. Dapro DF900 can be used as defoamer to reduce foaming in the pigment dispersion. Strontium chromate, an anti-corrosive pigment, improves the corrosion resistance. Red iron oxide imparts the colour, and has good heat resistance. Talc and barytes are extenders to reduce costs, ratios used depend on hiding power required. Ammonium benzoate prevents flash rusting. Viscosity and pH are adjusted with ammonia.
|
FORMULATION 7-20
|
nvc 50%
PVC 17.9%
Disperse the millbase fully and then let down with further resin. Plasticiser and coalescents are pre-blended before addition to minimise pigment flocculation. Dimethyl amino ethanol (DMEA) adjusts the pH. Rheology and viscosity are adjusted with Collacral PU85 (BASF, fatty acid ethoxylate urethane associative thickener) and Acrysol TT935 (Rohm & Haas, acrylic viscosity modifier). After formulating, the primer should be allowed to age to ensure sufficient migration of coalescents into the latex particles.
Johncryl 8210 from S. C. Johnson is the acrylic emulsion binder. Byk 181 (Byk Chemie) is an anionic acrylic dispersant. Surfynol 104E (Air Products) is a surfactant which helps to stabilise the dispersion. Foamex 7447 (Tego Chemie, polysiloxane emulsion) reduces foam in the pigment dispersing. Heucophos ZPZ (Heubach) is a zinc phosphate anticorrosive pigment. Bayferrox 130M (Bayer) is red iron oxide for colour. Blanc fixe (Ex Sachtelben) and Plastoriet M (Ex Plastoriet Werke) are cheap extenders. Kodaflex
TXIB (Eastman Kodak, 2,2,4-trimethyl-l,3-pentanediol diisobutyrate) helps to lower the MFFT of the resin.
Some typical topcoat formulations are given below:
|
FORMULATION 7-21
|
PVC 16%
Volume solids 36%
The millbase is high speed dispersed for 20 minutes before the let down components are added with stirring. Rheology is adjusted with the associative thickener. Water is then added to achieve the correct application viscosity. Methyl carbitol helps with pigment wetting, enhancing dispersion. The pigment dispersant, a carboxy functional acrylate neutralised with ammonia, ensures dispersion stability. Wetting agent, e. g. from Rohm & Haas, also helps pigment wetting. Defoamer used is usually silicone based. Foaming can cause a reduction in pigment grinding efficiency. Pigment provides the colour and opacity.
The main binder resin is usually an acrylic or styrene/acrylic emulsion. Water is the carrier solvent. Plasticiser is added to lower the MFFT of the coating. Glycol ethers improve the coalescence. Aqueous sodium nitrite solution acts as a flash rust inhibitor.
(iv) White Top Coat
|
FORMULATION 7-22
|
Properties
|
PVC |
14.3% |
|
nvc |
36% |
|
pH |
8.0 |
The millbase is dispersed in a Cowles disperser for 20 minutes before let down. Primal WL-81 (Rohm and Hass) is an aqueous thermoplastic acrylic resin, 41.5 %nvc with a MFFT of 57°C. It does not contain co-solvents, which maximises formulating latitude. It can be crosslinked with monomeric methoxy melamines, e. g. Cymel 303, to give harder, more resistant films.
Viscosity can be adjusted for different application methods, such as spray and brush, without external thickeners, which often detract from resistance properties, by the addition of amines. Less volatile amines result in slower hardness development. Under high relative humidity drying conditions, morpholine is superior for sprayability.
Under low humidity or high air flow conditions, Texanol may be eliminated. Butyl glycol is a very good coalescent for Primal WL-81, but it can be combined with other coalescents for optimum applicational characteristics. Dispersants can affect gloss and resistance properties. Orotan 165 is recommended.
(v) Waterborne White Industrial topcoat*16*
|
FORMULATION 7-23
|
nvc 30%
pH 8.2
Viscosity 25 secs @ 25°C DIN 4
PVC 18%
Disperse the titanium dioxide 2190 ( Ex Kronos) in Orotan 165 (Rohm & Haas, anionic dispersant) and Disperse Ayd W22 (Daniel Products, surfactant), with water as carrier. Antifoam (Byk 035 from Byk Chemie) and flash rust inhibitor (Emadox NA from Labema) are added. When dispersed, add the pigment paste to the let down mix. Add butyl benzyl phthalate plasticiser and Dehydran 1293 (modified polysiloxane defoamer from Henkel, to reduce foam formation on application) and mix well. Adjust viscosity with water. Neocryl A633 is a 42%nvc acrylic/styrene dispersion from Zeneca. Silwet L-77 (Osi) is a nonionic silicone surfactant to improve wetting.
|
(v) Waterborne White Gloss Stoving Enamel
The acrylic resin is a water reducible resin of the type described in Chapter II. (vi) A Waterborne Acrylic Stoving Enamel |
|
FORMULATION 7-25 |
|
|
Mill Together Cymel 303 Tamol 731 butyl glycol dimethyl aminoethanol (DMEA) water rutile titanium dioxide |
5.880 0.466 1.490 0.093 9.790 19.590 |
|
Add with stirring: Acrysol WS-68 dimethylaminoethanol (15% aqueous) p-toluene sulphonic acid (10% aqueous) |
60.641 1.490 0.560 |
|
Total |
100.00 |
|
Properties PVC 40% |
|
The finish is applied by spraying and stoved at 150°C for 30 mins. |
Acrysol WS-68 is a small particle size emulsion of an acrylic copolymer containing acid groups which solubilise the polymer when the amine is added. Cymel 303 is ’monomeric’ melamine-formaldehyde resin which crosslinks the acid groups in the acrylic copolymer. The p-toluene sulphonic acid catalyses the crosslinking reaction after the DMAE evaporates during the stoving operation.
This example is one which indicates a variety of approaches possible for the important field of industrial stoving finishes, for which alkyd, urethane, epoxy, polyesters and cellulosic formulations are also used. Other examples have been given in this book in the solvent based section, including a vinyl chloride stoving enamel (thermoplastic section ) and an acrylic stoving enamel (thermoset section ). It must be stressed that there is no best product. They are different and have both advantages and disadvantages which may vary according to the end use. The water based acrylic is the cheapest of the three finishes, but it can give poor adhesion because of wetting problems. The solvent based acrylic gives good all round properties, but both the crosslinked enamels ( waterborne and solvent based) liberate formaldehyde on curing for which there is a limit of 1 ppm in air. Some organisations will not allow any formaldehyde based products on their sites. The vinyl resin recipe is expensive because of the relatively large solvent content, but it has no undesirable properties, and of the three examples, it is the easiest to recoat.
Water soluble melamine resins are used to cure aqueous alkyds, acrylic, epoxies and polyester resins, by exactly the same chemistry that is discussed earlier in this chapter.
Fully methylated hexamethylol melamines, which are extensively used in waterborne metal coatings, have the generalised structure shown in Figure 7-21.
CH3 — О—CH2—N — CH2OCH3
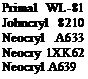 |
 |
Figure 7-21: Structure of Methylated Hexamethylol Melamine Resins suitable for metal protection formulations include :
 10 октября, 2015
10 октября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 