Transfer to monomer can occur in one of two ways. Both involve an abstraction process through which a hydrogen atom is transferred to the propagating chain. The free radical is transferred to the monomer to form a monomer radical.
a)
Abstraction from the Vinyl Carbon Atom.
The monomer radical formed is free to initiate the propagation of another polymer chain.
The newly propagated chain will have an unsaturated end group. This end group is available for re-initiation.
Propagation will lead to the formation of a branched polymer chain.
R — CH — CX -£cH2— CHX^- R + mCH2 = CHX
R — CH2— CX -£cH2-CHx||- R
[ch2— СНХІ L I Jm-1
CH,
CHX
Figure 1-11
b) Abstraction from a Side Chain
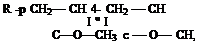
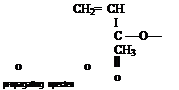 |
This type of reaction is typified by vinyl acetate, but may also occur with acrylic monomers with alkyl side groups.
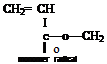 R — PCH— CH 4- CH, — CH2
R — PCH— CH 4- CH, — CH2
I " I
с—о—сн3 с—о—CH3
II II
terminated polymer chain
Figure 1-12
The free radical is on the side group of the monomer radical not the vinyl carbon atom.
Propagation can occur and, as in the case i) above, will result in a polymer with an unsaturated end group.
 20 июня, 2015
20 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 