The copolymerisation behaviour of three or more monomers can be predicted if the behaviour of the monomer pairs is known, by using an extension of the copolymer equation.
This can be illustrated for monomers Mb M2 and M3 as follows:
![]() = ki, i [Mi] [Mi] + кг, і [М2] [Mi] + кз, і [М3] [Mi]
= ki, i [Mi] [Mi] + кг, і [М2] [Mi] + кз, і [М3] [Mi]
—іг1 = кі,2 [Мі] [М2] + к2,2 [Мг] [М2] + кз,2 [Мз] [М2] dt
= кі,3 [МІ] [Мз] + кг, з [М2] [М3] + кз, з [Мз] [М3] dt
As with the two component system, although the radical concentration [M, ], [МІ] and [Mi] are unknown the steady state relationship can be derived in terms of M,, M2 and M3.
Hence we can define the relationship as
ki,2[Mi][M2] + кі,3[МІ][Мз] = кг, і[Мг][Мі] + кз, і[№][Мі]
кг, і[Мг][Мі] + кг, з[Мг][Мз] = кі, г[Мі][Мг] + кз,2[Мз][Мг]
кз, і [Мз][Мі] + кз, г[Мз][Мг] = кі, з[Мі][Мз] + кг, з[Мг][М}]
|
Ш + Ш Г1,2 1*1,2 ’ R1 [Ml] + [M2] |
|
R2 [Ml] + [M2] |
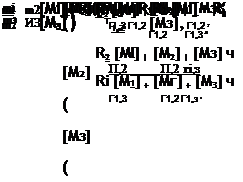 |
![Terpolymers and Multi-Component Systems Подпись: ( Ri [Mi] + [Мз] ) ( R2 [MI] + [M2] )](/img/1207/image129.png) |
For a case where all the monomers can react with each other this can be reduced to
![]() k-i, i
k-i, i
кі, з
k2,2
кг,1
кг,2 кг. з
кз, з
кз,1
кз, з
кз, г
кг, і
кг, з
кз, і
кз, г
1. Q and е Values
An alternative approach to the use of reactivity ratios is the use of Q and e values.
This system was developed to take account of the tendency of monomers to form alternating copolymers. The Q and e values can be taken to represent the relative rates of reaction of various monomers to each type of free radical after correction is made for differences in general monomer reactivity.
The reciprocal of the monomer reactivity ratio l/r, can be considered as the monomer reactivity which relates the relative reactivity of like and unlike monomers with the propagating species.
The structure of a monomer has a profound effect on its reactivity, e. g. a phenyl group adjacent to a double bond increases the reactivity more than that for a methyl group. This is due to the greater degree of resonance stabilisation obtained. The contribution made by the structure and steric factors, to the overall reactivity of the monomer, is represented by Pi and Qi.
![]()
Pi relates to the reactivity of the radical Mi Qi relates to the reactivity of the monomer Mi
The polarity of the double bond also influences the monomer reactivity and is represented by Єї and e2.
where: et and e2 relate to the residual electrostatic charge in the respective reacting
species.
Ei and E2 represent charges on Mi and М2 D is the di-electric constant К is the Boltzman constant
X is the distance separating the charges in the activated state.
Assuming that e; is the same for M — and M;
ki, i = P1Q1 exp (-e?)
kl,2 = P1Q2 0ХР (-Є1Є2)
then
n = (Qvb2) охр (—Є1 (Є1 — Є2)) and
Г2 = <Q^Qi) 0XP (—02 (02 — 01))
thus:
ПГ2 = exp (-(Є1-Є2)2)
Values for Q and e can be taken from published tables and listings and used to calculate the reactivity ratios for the particular monomer pairs under consideration.
 28 июня, 2015
28 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 