Figure 1-40
(vii) Reaction of Carboxyl Containing Polymers with Alkoxyl Methyl Ether Groups
G-OH + RO — CH2— NH —I —► C — 0 — CH2— NH —| + ROH
0 0
Polymer backbone шштт Acrylic polymer backbone AAArV
Figure 1-41
Where RO-CH2-NH- may be the alkoxy methyl ether of an acrylamide polymer or of a melamine or urea formaldehyde resins.
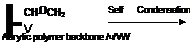 |
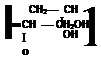 |
Figure 1-42
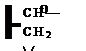 |
 |
|
(x) Reaction of Glycidyl Containing Polymers with Amine Groups
Polymer backbone
Figure 1-43
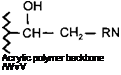
This reaction can be used as an alternative way of introducing a hydroxyl group to an acrylic polymer backbone. They are of particular interest where the use of a hydroxy monomer is not technically feasible. They can also be of use in circumstances where a more even distribution of the OH groups along the polymer backbone is desired, since the distribution using this technique can often be more uniform than when a hydroxy monomer is used to introduce OH functionality.
(xi) Reaction of Glycidyl Containing Polymers with Amino Formaldehyde Resins
Figure 1-44
This reaction requires an acid catalyst.
![]()
|
|
|
 26 июня, 2015
26 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 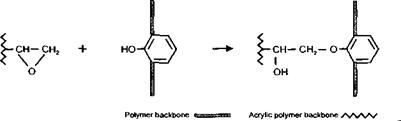
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 