A large number of multifunctional isocyanate curing agents are commercially available for crosslinking of the hydroxyl functional resin. These isocyanate adducts are mostly derived from a limited number of aliphatic and aromatic monomeric isocyanates, whose structures can be seen in Figure 5-2.
|
TDI — toluene diisocyanate
|
|
MDI — diphenyl methane diisocyanate
HMDI — hexamethylene diisocyanate |
^vvw
NCO
IPDI — isophorone diisocyanate
OCN’-‘ NCO
|
TMXDI — tetramethylxylene diisocyanate NCO NCO
Figure 5-2 Common Diisocyanates |
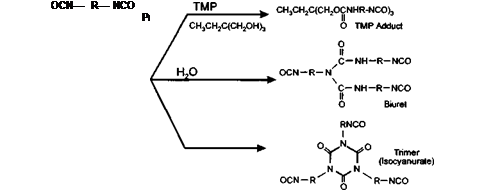 |
The chemical reactions used in preparing the commercial curing agent is either via trimerisation or reaction with water or a polyol (see Figure 5-3), followed by distillation to remove excess monomer.
The final distillation stage is extremely important in order to ensure removal of any low molecular weight volatile monomeric isocyanates.
An aromatic based polyisocyanate, such as toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is significantly more reactive than aliphatic isocyanates, producing films which are very hard and exceptionally resistant to a range of highly aggressive chemicals. However, aromatic polyisocyanates are also characterised by very poor stability to ultra violet light, resulting in discolouration and chalking. Hence, aromatic based poly isocyanates are normally used in interior applications such as wood finishing, and primers. Due to its toxicity and ability to sensitise individuals to isocyanates, TDI is normally used in an adducted or modified form.
An aliphatic based polyisocyanate, such as hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI), although slower to cure than its aromatic counterpart, displays superb stability to UV light and as such is found in the widest range of applications. However, HMDI is volatile and extremely toxic. Its use as HMDI is very limited to closed handling systems. The use of dimers or trimers as adducts of HMDI is much safer due to their lower volatility and as such these are often used in place of the HMDI monomer.
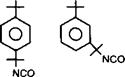
Although tetramethylxylene diisocyanate (TMXDI) also bears an aromatic structure like the TDI based products, it shows greater durability as the isocyanate group is not directly attached to the aromatic ring.
Isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI) based isocyanate curing agents confer very high durability to 2 component polyurethane systems, but this is offset by poor flexibility and low reactivity. Hence IPDI adducts are usually combined with flexible hydroxy prepolymers in low bake applications. They are also used as partial replacements for the aromatic or aliphatic polyisocyanates. Compared to other diisocyanates, IPDI has the advantage that it has relatively low volatility, whilst still being a liquid.
The major suppliers of isocyanate curing agents and their respective trade names can be seen in the following table.
|
TABLE 5-1: MAJOR SUPPLIERS AND TRADE NAMES OF ISOCYANATES
|
Low viscosity 100% isocyanate prepolymers are also now available for use in high solids coatings. Although a range of new isocyanate raw materials has been developed with this purpose in mind, hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) has formed the basis of a number of commercially available products<2,3). This is due to the lower viscosity of prepolymers of HMDI when compared to the other main isocyanate raw materials, as shown in table
2. The formation of a trimer<4) (isocyanurate) has been the preferred route over the biuret or adduct due to its lower tendency to hydrogen bonding and lower solution viscosity. Commercially available products following this route include Desmodur VP LS 2025 and VP LS 2103.
|
TABLE 5-2: COMMERCIAL POLYISOCYANATES
|
 26 августа, 2015
26 августа, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 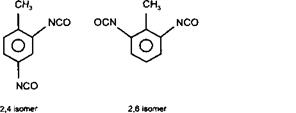
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 