|
TABLE 1-4: THE MAJOR ACRYLIC MONOMERS Monomer Chemical Formula Homopolymer
|
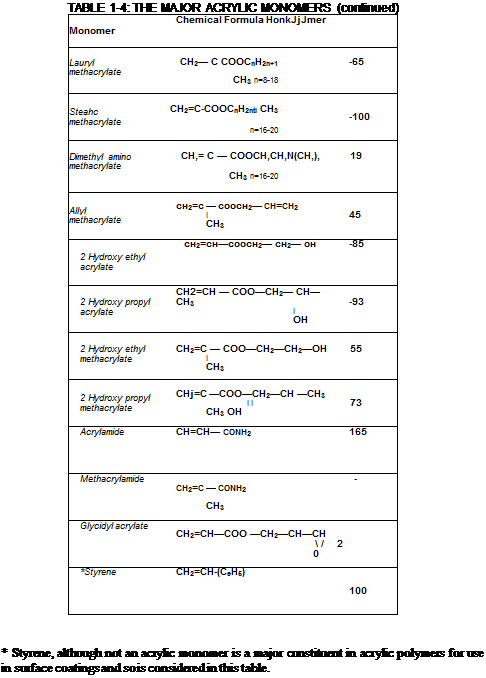 |
Of particular importance in surface coating applications are the two series of related monomers derived from acrylic acid and methacrylic acid. These monomers are termed “acrylates” and “methacrylates” respectively and polymers derived from either species are known collectively as acrylic resins. Typical acrylate and methacrylate monomers are shown in the table above.
Acrylic esters have the common structure:
CH2=CH
COR
О
Figure 1-21
Whilst methacrylic esters have the common structure:
I
II
Figure 1-22
Typical examples are:
Butyl Acrylate Butyl Methacrylate
Figure 1-23
Various types of functionality can be built into acrylic and methacrylic esters which can be introduced into the final acrylic polymer. Typical functionality includes hydroxyl, carboxyl, amide and epoxy groups.
 24 июня, 2015
24 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 