A moisture-curable urethane resin is simply a urethane prepolymer with free — NCO groups. Typically made from aromatic isocyanates, the free — NCO group of such a resin, when exposed to the environment after application, will react with ambient moisture and produce urea linkages between prepolymer chains, resulting in formation of the cured coating (Figure 2.64).
The type of isocyanate, MW and — NCO functionality are controlled to balance drying time and film properties. The drying time is signi-
|
Figure 2.64: Schematic representation of curing of moisture-curable urethane system |
ficantly dependent on the ambient moisture content, temperature and film thickness. Coatings applied at higher film thickness under high humidity frequently show a bubbling defect due to formation of CO2 gas during curing that gets trapped in the film. Due to free — NCO content, such systems have limited shelf-life.
 20 октября, 2015
20 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 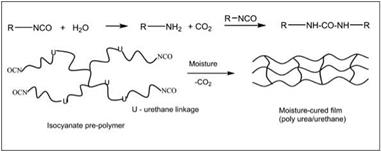
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 