Mannich bases are derived by reaction of phenol, formaldehyde and an aliphatic or cycloaliphatic polyamine. These curing agents show enhanced reactivity due to the catalytic effect of phenolic hydroxyl. Phenalkamines are similar products using alkyl phenols (Figure 2.50). Cardanol-based phenalkamines are very popular products used in marine and protective coatings. These types of curing agents are known for their excellent low temperature curing (up to 0 °C) characteristics even in damp conditions. They exhibit better compatibility, excellent blush resistance and excellent chemical resistance along with good wetting, adhesion and surface tolerance properties.
Ketones can reversibly react with primary amines with the loss of water to give ketimines (Figure 2.51). They can be considered blocked
|
|
Figure 2.51: Ketimine chemistry
polyamines. Absorption of atmospheric moisture during and after application of the coating produces a ketone and a polyamine.
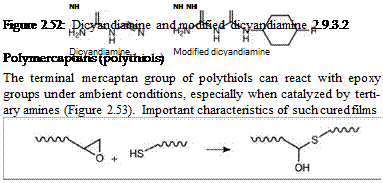
Dicyandiamine is a crystalline solid (melting point 207 °C) that is incompatible with epoxy resin at room temperature. It is used as a cross-linker for epoxy powder coatings. However, the reaction of dicyandiamide with the epoxy group proceeds differently from the classical amines, as the primary adducts undergo different chemical rearrangements. They are frequently modified to improve solubility in epoxy resins (Figure 2.52).
include good flexibility and adhesion. They are not frequently used in coatings due to the strong sulfurous odor of thiols, but are more commonly used in adhesives, sealants and civil engineering applications.
 10 октября, 2015
10 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 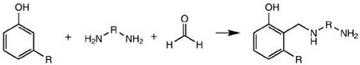
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 