Polyurethane coatings, one of the most important coating systems among the modern high performance coatings, are two-component systems based on polyols and isocyanates. Curing occurs
|
|
at ambient temperature. Aliphatic polyisocyanate-based systems react more slowly than aromatic ones, and therefore, they need to be catalyzed. The catalysts used for polyurethane systems can be broadly categorized as tertiary amines and metal catalysts. Some of the important ones are described below, with examples shown in Figure 5.12.
While dibutyltin dilaurate has been the most commonly used catalyst over the years, it is being replaced by safer alternatives such as bismuth and zinc carboxylates. Zirconium-based catalysts are preferred in waterbased two-component systems because of their better selectivity for isocyanate-hydroxyl reactions over isocyanate-water reactions.
 13 января, 2016
13 января, 2016  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 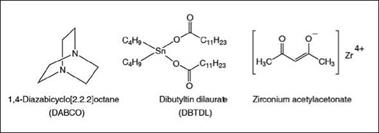
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 