Adhesion is a key property of coatings and can influence many other mechanical and performance properties. Adhesion can be defined
 as the resistance of the coating film to mechanical separation from the substrate. While the nature of the binder is the primary factor influencing adhesion, it can be improved by the use of additives called adhesion promoters. Characteristics of the substrate are also very important factors governing adhesion.
as the resistance of the coating film to mechanical separation from the substrate. While the nature of the binder is the primary factor influencing adhesion, it can be improved by the use of additives called adhesion promoters. Characteristics of the substrate are also very important factors governing adhesion.
Adhesion of a coating film to the substrate can be improved by mechanical surface treatments such as sanding or grit blasting, as well as other surface treatments such as chemical etching, flame treatment, plasma treatment or conversion coatings. In circumstances where these methods are not possible, improvements in adhesion must be achieved through careful selection of components in the paint formulation and using adhesion promoters.
Adhesion is a complex phenomenon involving physically and chemically induced intermolecular interactions at the coating-substrate interface. Almost all adhesion promoters work through a common mechanism associated with their unique molecular structure, which essentially contains two different functional groups, one of which can react with the substrate and the other with the polymer matrix of the coating film. This results in a chemical bridge between the two through strong covalent bonds, which improves the adhesive strength.
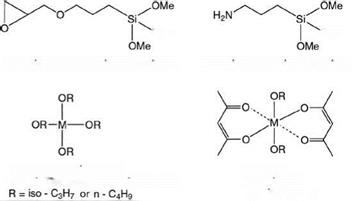
Because of a wide variety of coating systems and various types of substrates, it is impossible to have a single additive that may be used universally in all systems. Typical classes of commercially available adhesion promoters are organofunctional silanes, tita — nates, zirconates, zircoaluminates, alkyl phosphate esters, amides, imines and metal organic complexes. Some examples are shown in Figure 5.11. They all have their own merits and demerits. Silanes, titanates and zirconates are available with a wide range of organic modifications and have excellent solubility in organic solvents, but they are sensitive to water to varying degrees. Zircoaluminates, alkyl phosphate esters and metal organic complexes are less water sensitive but have limited solubility in organic solvents. The choice of the most suitable adhesion promoter, therefore, will depend on the type of polymer and substrate in question.
 10 января, 2016
10 января, 2016  Pokraskin
Pokraskin  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 