One-component baking types of coatings in which resins such as alkyd, polyester, hydroxyl functional acrylic or epoxy esters are cross-linked with amino resins are typically catalyzed by acid catalysts. Strong acid catalysts such as sulfonic acid and phos-
|
Figure 5.14: Acid catalysts for amino-cured backing systems |
phoric acid are generally used. Even though less reactive hexame- thoxymethyl melamine resins are used in coatings, the curing rate can be accelerated significantly by use of a strong acid catalyst. Different types of acid catalysts varying in their acid strength are commercially available. The type and amount of catalyst is determined by the curing conditions of the coating, such as specific sto — ving temperature and time. High acid strength and high addition levels negatively impact their storage stability. The storage stability of coatings with a strong acid may be improved by blocking the acid group with amines to form a salt. At higher temperature curing, the amine evaporates and acid is released, triggering its catalytic effect. Some important examples of such a catalyst are shown in Figure 5.14.
 16 января, 2016
16 января, 2016  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 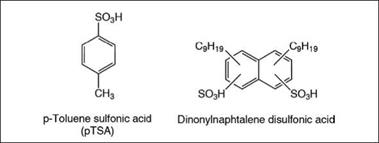
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 