3.4.5.1
Occupational Health
Precautions have to be taken and workplace concentration limits have to be observed when handling lead chromate and lead chromate pigments. MAK or Occupational Exposure Limits for lead chromate and lead chromate pigments themselves are not given.
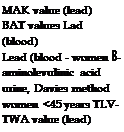 |
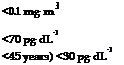 |
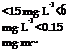 |
|
General regulations exist for all lead-containing materials. Concentration limits are as follows:
It is accepted that the BAT limit has been complied with if the blood lead level does not exceed 50 pg dL-1 (or for women of <45 years, 30 pg dL-1).
Council Directive 82/605/EEC specifies maximum lead concentrations in the air of <150 pg m-3 and permitted blood lead levels of 70-80 pg dL-1, with 8-aminolevulinic acid values of 20 mg g-1 creatinine [3.135, 3.136].
Additionally the TRK value/TLV-TWA value for chromium(VI) compounds of
0. 05 mg m-3 calculated as CrO3 in total dust has to be complied with [3.137].
Lead chromate and lead chromate pigments are classified as toxic for reproduction (Unborn child: Rep. Cat. 1/category RE 1, Fertility: Rep. Cat. 3/category RF 3) and carcinogenic (Carc. Cat. 3/category C 3 [3.135, 3.138].
As far as carcinogenic effects are concerned, extensive epidemiological investigations have given no indication that the practically insoluble lead chromate pigments have any carcinogenic properties [3.139, 3.140]. Such properties have been reported for the more soluble zinc chromate and strontium chromate pigments.
Lead chromate pigments can be safely handled if the various rules and regulations regarding concentration limits, safe-working practices, hygiene and industrial medicine are adhered to.
3.4.5.2
 13 ноября, 2015
13 ноября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 