Phthalocyanine complexes have been synthesized with nearly all the metals of the periodic table [18,35,36]. Despite the apparently complex structure of the Pc system, it is formed in a single-step reaction from readily available starting materials. The reaction is strongly exothermic. For example, the synthesis of CuPc from phthalodinitrile (4CgH4N2 + Cu <Pr> C32H16N8Cu) has a reaction enthalpy
of -829.9 kJ/mol. The low energy of the final product can be accounted for by resonance stabilization; this explains at least partially the relatively facile formation of the complex. The most important metal phthalocyanines are derived from phthalodinitrile, phthalic anhydride, Pc derivatives, or alkali metal Pc salts.
From o-Phthalonitrile.
where M is a metal, a metal halide (MX2), or a metal alkoxide [M(OR)2]. The reaction is carried out in a solvent at ca. 180 °C or by heating a mixture of solid reactants to ca. 300 °C.
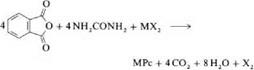 |
From Phthalic Anhydride.
This synthesis is carried out either in a solvent at 200 °C or without solvent at 300 °C.

Fromphthalimide derivatives, e. g., diimidophthalimide:
Metal-free phthalocyanine is obtained by the following procedures [15,35-37].
1) Decomposition of an unstable MPc with alcohol or acid PcNa2 + 2H3O+ ^ PcH 2 + 2 Na+ + 2 H 2O
2) Direct synthesis (e. g., from phthalodinitrile).
Syntheses of MPc from phthalodinitrile or phthalic anhydride in the presence of urea are the two most important laboratory and industrial methods. They were also used originally by Linstead et al. [8,9]. This procedure allows the production of many phthalocyanine compounds [35-37]. Catalysts such as boric acid, molybdenum oxide, zirconium and titanium tetrachloride, or ammonium molybdate are used to accelerate the reaction and improve the yield [36,37]. Ammonium molybdate is especially effective. Reaction is carried out either in a solvent or by heating the solid components. When metal chlorides and phthalodinitrile are used as starting materials, the reaction products are partially chlorinated (e. g.,7).
|
|
Lowering the reaction temperature or adding urea or basic solvents decreases the extent of chlorination. Solvents such as nitrobenzene, trichlorobenzene, alcohols, glycols, pyridine, and aliphatic hydrocarbons are employed. By using substituted phthalic acids such as 4-chlorophthalic acid anhydride, 4-sulfophthalic acid anhydride, or 4-nitrophthalimide, phthalocyanines with inner substitution can be produced. The products can often be purified by sublimation in vacuo at 300400 °C. Soluble Pc’s can be purified by recrystallization.
 29 августа, 2015
29 августа, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 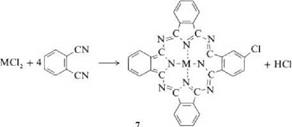
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 