Cationic dyes carry a positive charge in their molecule. The salt-forming counterion is in most cases the colorless anion of a low molecular mass inorganic or organic acid. Many of these dyes can be converted into water-insoluble dye bases by addition of alkali. For this reason, they were formerly called basic dyes; although still in use today, the term should be abandoned.
The positive charge of cationic dyes may be either localized or delocalized. In 1, the positive charge is localized on an ammonium group:
|
|
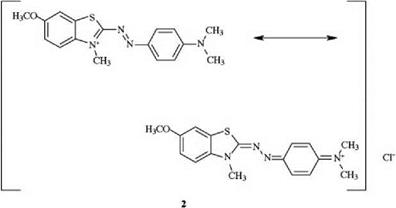
In the diazahemicyanine dye 2, the positive charge is delocalized across the dye cation.
|
|
As in these examples, the charge-carrying atom is usually nitrogen, but in some dyes this function is adopted by an oxygen, sulfur, or phosphorus atom.
 25 августа, 2015
25 августа, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 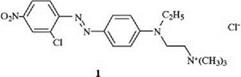
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 