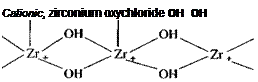
Organometallic compounds based on zirconium are actively being promoted as adhesion promoters and are claimed to function as coupling agents. Zirconium compounds appear to have widespread potential for use in the polymer industries since they exist in both water and organic solvent-soluble forms. The aqueous chemistry is dominated by hydrolysis, depending on zirconium and hydrogen ion concentration and the nature and concentration of anions present. Depending on the ligand present the polymeric species in solution can be cationic, anionic, or neutral [17]. Simplified structural representations of polymeric zirconium species are shown in Fig. 1
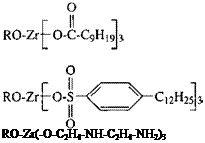
Solvent soluble compounds include zirconium acetylacetonate, zirconium methacrylate, and the family of neoalkoxyl zirconates. Some commercially available zirconates are shown in Table 3. Wang [8] has described the synthesis of a soluble linear Schiff base zirconium-based coordination polymer (N, N’, N’", N»’-tetrasalicylidene-3,3′-diaminoben — zidene) zirconium, and other hybrid copolymers, and has demonstrated improved adhesion on glass and aluminum substrates for poly(methyl methacrylate), polyethylene, and polypropylene when used as hot-melt compounds.
 |
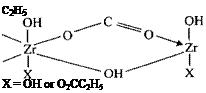
Studies on a reactive PVA copolymer (commercial vinyl alcohol), vinyl acetate copolymers stabilized by N-methylol acrylamide, and unreactive PVA homopolymer emulsions have shown that the resistance of these materials to cold — and boiling-water immersion tests can be improved considerably by the addition of zirconium oxychloride, zirconium-hydroxychloride, and zirconium-nitrate. These improvements in water resistance are considered to occur in the former cases by interaction between polynuclear
осо? oco2 oco2
OAc
Chemical Description
![]()
![]()
 Neoalkoxytrisneodecanoyl
Neoalkoxytrisneodecanoyl
zirconate
Neoalkoxytris(dodecanoyl)benzene sulfonyl zirconate
Neoalkoxytris(ethylenediaminoethyl)
zirconate
Neoalkoxytris(m-aminophenyl)
zirconate
Zirconium propionate zirconium species and functional groups on the polymer and in the latter by reaction with the colloidal stabilizer. In these cases the zirconium compounds are functioning by an insolubilization process rather than as an adhesion promoter per se, but the end result is an increase in wet adhesion [45].
Other zirconium-containing coupling agents are the zircoaluminates, which are described in the technical literature [46] as inorganic polymer backbone materials of low molecular mass containing specific atom ratios of zirconium and aluminum with two organic ligands: one for overall molecular stability and the second to confer organo functionality; The commercial range includes amino-, carboxy-, and methacryloxy — functional compounds. It is claimed that the addition of these materials to adhesives and surface coatings improves their wet adhesion materially [47].
 3 июля, 2015
3 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 