The universally accepted method for testing adhesion under shear is a static load test [21], where a known surface area of the adhesive-coated product is applied under controlled
|
|
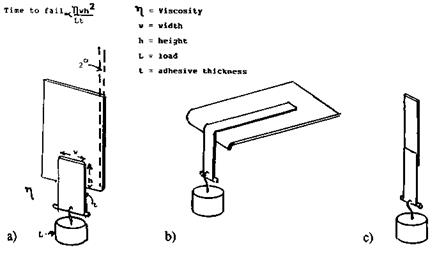
conditions to a standard test surface, usually stainless steel or a standard cardboard, or even the product’s own backing. Then this is secured vertically, plus a 2°tilt-back, to prevent any possible low-angle peel. A fixed load is then applied (Fig. 7a), and the time taken for failure is recorded or any slip that occurs in a given time measured. A trip mechanism can be set up so that the falling weight stops a stopclock to denote the failure time. This test can be carried out at elevated temperature; variations of the basic concept exist, such as mounting the test surface horizontally [22] with a small radius of curvature at the edge of the test panel to redirect the tail of the tape under test to the vertical, in order to hang a suitable load (Fig. 7b). A further variation, used in the electrical industry to measure adhesive thermoset characteristics, is a high temperature shear test [23], where a controlled area overlap bond is formed, usually 0.5in. (12mm) by 0.5in. (12mm), either face to face, or face to backing. The adhesive is then given a thermoset cycle, followed by a high temperature shear test (Fig. 7c).
While a static load test is the commonly accepted procedure, in practice many variations in areas and weights are used, to compensate for the various qualities of adhesive evaluated, so that the test results will fall into a similar time frame, so it becomes difficult to compare different adhesive systems from accumulated data. It has the disadvantage of giving variable results for the same adhesive system, and is essentially a pass/ fail test, as many products remain in place at the end of the test period. Experience has shown that the shear properties of pressure-sensitive adhesives to porous and nonporous substrates can be quite different, and each must be judged on its own merits.
|
Figure 7 Shear testing: (a) 178° shear; (b) horizontal shear; (c) overlap shear. |
 7 июля, 2015
7 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 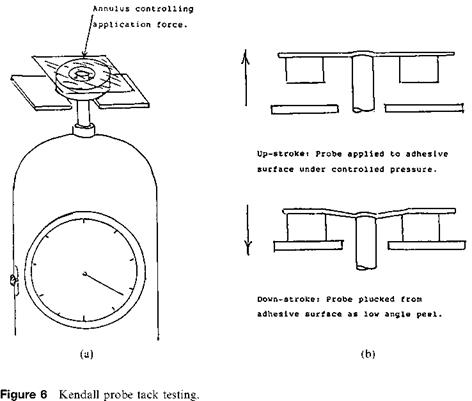
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 