For phenolic FRP-wood bonded assemblies, the following factors relating to the performance of the bonded interface were investigated: (1) the influence of coupling agents, (2) the influence of clamping pressure, and (3) the influence of open/closed assembly time. The sizes of the specimens used were smaller than those specified in ASTM D2559. Each laminated FRP-wood assembly for the delamination test consisted of four pieces of red maple wood and two pieces of FRP strips; four wood pieces [each 19.05mm x 76.2mm x 609.6mm (0.75" x 3" x 24")] were placed at the center of the
|
Figure 3 Manufacturing of bonded FRP-wood delamination specimens (after Ref. 4). |
lamination, and FRP strips (each 4.76mm x 76.2mm x 609.6mm (3/16" x 3" x 24")] were located at the top and the bottom of the lamination (Fig. 3). Wood-wood assemblies for the delamination test were made by bonding six wood pieces [each 19.05 mm x 76.2mm x 609.6mm (0.75" x 3" x 24")]. For some of the FRP-wood samples, the wood surfaces to be bonded to the FRP strips were primed with the coupling agent (HMR) following the guidelines given by Vick [9]. The HMR primer was spread with a brush at approximately 0.147 kg/m2 (0.03 lb/ft2) on the wood surfaces, and the primed surfaces were dried for 24 hours. All wood boards were conditioned to 12% moisture content (MC) before bonding. The adhesive, either resorcinol formaldehyde (RF) or phenol resorcinol formaldehyde (PRF), was applied with an electronic spreading roller to maintain a constant spread rate of 0.0294 to 0.0392 kg/m2 (0.006-0.008 lb/ft2) as recommended by industry. Each of the laminated wood-wood and FRP-wood beam-type members was cut into six 3-inch long specimens, and these specimens were tested following the ASTM D2559 guidelines. To study the influence of key parameters on the bond performance, six wood-wood and either 12 or six FRP-wood samples were tested for each combination of coupling agent, clamping pressure, and assembly time.
The effect of the HMR coupling agent on delamination performance was studied first [4]. The specimens without HMR primer showed a small percent delamination (<3.0%) for phenolic FRP-wood interfaces, and in general, the specimens without HMR exhibited less delamination of wood-wood interfaces, particularly at layers adjacent to the phenolic FRP (see Tables 1 and 2). For face bonding of phenolic FRP-wood laminates, the fabrication parameters related to clamping pressure and open/closed assembly time could be easily controlled. The study of these parameters (Tables 3 and 4) indicated that specimens fabricated with high pressure [p = 1.448 MPa (210 psi)] and intermediate open/closed assembly times (t = 5/30 min) showed the least delamination along both the wood-wood and phenolic FRP-wood bondlines; therefore, for the RF adhesive used to bond the red maple wood and phenolic FRP composite in this study, the combination of 1.448 MPa (210 psi) for clamping pressure and 5/30 minutes open/closed assembly time is recommended.
 14 июля, 2015
14 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 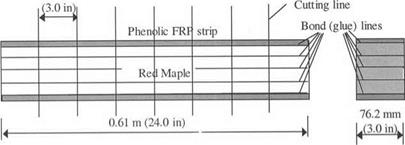
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 