In the case of organic-inorganic materials interaction (e. g., polymer-metal oxide), Bolger and Michaels [33] suggested a model based on Bronsted acid-base chemistry to account for the strength of the interaction. They defined a parameter A for organic acids and bases:
|
Aa = IEPS(B) — pKa(A) |
(7a) |
|
and |
|
|
Ab = pKa(B) — IEPS(A) |
(7b) |
where the Ka is the dissociation constant of the organic species and IEPS* the isoelectric point of a solid, namely the metal oxide (see XPS, Section IV. C.l. a).
Bolger and Michaels identified three regimes of acid-base interactions:
(i) A ^ 0: negligibly weak acid-base interactions
(ii) A « 0: acid-base interactions of comparable forces to those due to dispersive interactions
(iii) A > 0: strong acid-base interactions perhaps resulting in chemical attack or (metal) corrosion.
Table 5 reports A parameters for acetic acid (pKa(A) = 4.7) and methylamine (pKa(B) = 10.6) interacting with SiO2, Al2O3, and MgO, whose IEPS values are 2, 8, and l2, respectively. The maximum positive values of A are obtained for the amine-SiO2 and carboxylic acid-MgO interactions, thus for acid-base adducts. In
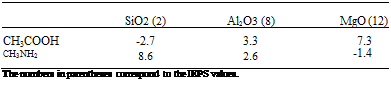
contrast, Д is negative for the carboxylic acid-silica and amine-MgO interactions as they are of the acid-acid and base-base types, respectively.
Bolger’s concept has successfully been used to interpret the failure mechanisms of polyimide/MgO joints [51]. Similarly, a ДА value of 6.5 was estimated for the interaction of PMDA-ODA PAA [pyromellitic dianhydride-oxydianiline poly(amic acid), pKa(A) = 3] with copper (IEPS of copper oxide = 9.5); this is a too strong predicted interaction, suggesting the migration of copper in the polymer film [52].
 23 июня, 2015
23 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 