The ring closure to an isatin derivative takes place only under certain, accurately controlled conditions. It is important that the reaction be carried out in hot sulfuric acid.
In the course of 15 minutes, 200 grams of pure, dry, finely divided “thioamide” is added to 800 grams of 94 per cent sulfuric acid (66° Be) at a temperature of exactly 94°C. Considerable heat is generated and the mixture must be cooled. When the mixing is complete, the mixture is heated at 106-108° for one hour, after which no more sulfur dioxide is evolved. The solution is then cooled to 20°, and the product is converted to the hydrochloride of a-isatinanilide by pouring it in a thin stream into a well stirred mixture of 1 liter water, 2 kilograms of ice, and 500 grams of salt. The hydrochloride of a-isatinanilide separates as a light reddish brown precipitate mixed with finely divided sulfur.
If the anilide is to be purified, it is filtered off and washed thoroughly with 20 per cent salt solution. The salt, freed from acid, is stirred with water containing enough soda to give a weakly alkaline reaction, and the solid mixture of the anilide and sulfur is again filtered off, washed thoroughly, and dried. It is then extracted with cold carbon bisulfide (removing the sulfur), and finally crystallized from alcohol. The purified material is in the form of dark colored needles melting at 126°C. The yield is about 150 grams of pure material from 200 grams of “thioamide.” When the anilide is heated with a small excess of dilute hydrochloric acid, the aniline group is split off as aniline, and pure isatin, melting at 200-201°, is precipitated. It may be recrystallized from hot water in which it is very soluble.
Isatin is used as such in the preparation of many valuable vat dyes. Still more important are the vat dyes preparea directly from a-isatinanilide by condensation with 0-hydroxythionaphthenes. As first observed by G. Engi, isatin and a-isatin — anilide lead to different dyes on condensation. In the case of isatin itself, the f) group is reactive in the condensation reaction, while with a-isatinanilide, aniline is split out and a condensed dyes are formed. These a condensation products are much more valuable as dyes than the isomeric f) compounds.
|
 21 декабря, 2015
21 декабря, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 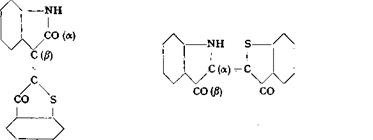
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 