1.2.2.1. Introduction
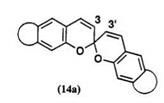
A number of spirobenzopyranobenzopyrans, 14, in which two ben — zopyran components are linked via 2-spiro carbon, were prepared in the 1960s and 1970s.1,48 These compounds are also called spirodibenzopyrans or dichromenes, and they exhibit photochromic properties (Scheme 9). Four geometrical isomers for colorless forms can theoretically exist for spirodibenzopyrans having different substituent groups at the 3,3′-positions. Isolation of these isomers has been attempted, but only one isomer has been isolated by general workup.1,49
 |
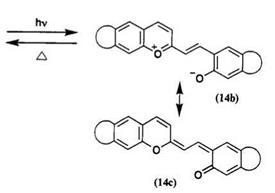 |
The photocolored form is assumed to form via the heterolytic cleavage of the C—O bond. Studies on the thermal fading kinetics have shown 2,50
that the closed form is thermally stable at room temperature. Comparison between spirodibenzopyran and spiroindolinobenzopyran shows that the thermal fading rate of the photocolored form is almost similar in both series. The steric hindrance of a substituent group on the 3- and/or 3′-position of spirodibenzopyran affects the thermal fading rate of the colored form. Thermal fading is also affected by the substituent groups and annelated benzopyran. The thermal fading rate constants for 3-substituted derivatives are in the range of 2.0 to 3.75 x 102s-1 at 25°C in toluene.
 24 июня, 2015
24 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 