The coordination chemistry of formazan dyes has been extensively reviewed in Venkataraman’s classic treatise on synthetic dyes,374,375 and more recently in Wilkinson’s treatise on coordination compounds.376
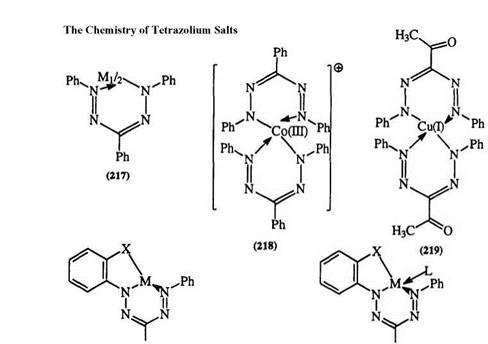
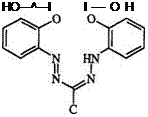
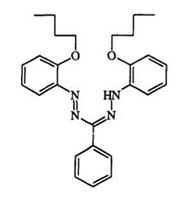
1,3,5-Triphenylformazan behaves as a bidentate ligand forming 2:1 complexes (217) with divalent copper, nickel, and cobalt.377 Formazan metal complexes can be compared to complexes of azo dyes or beta diketones due to structural similarity.301,302 In general, formazan metal complexes have low stability toward acids. However, when electron-donating substituents are added to the aromatic ring, a considerable enhancement in stability is observed. Cationic complexes of type 218 are also known. The complexation of formazan with metal cation can be accompanied by oxidation to the tetrazolium salt and the formation of a complex
|
|
|
|
|
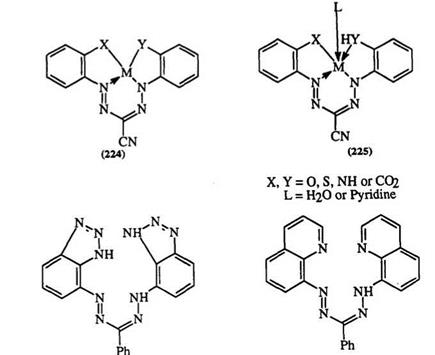
A variety of complexes, e. g., 224 and 225, can be formed from the tetradentate formazans.384,385,388-396 Tetradentate formazans containing heterocycles, e. g., 226 and 227, also form metal complexes.385
 |
 |
The bulk of the literature on the coordination chemistry of forma — zans deals with complexes of copper, nickel, cobalt, and chromium.
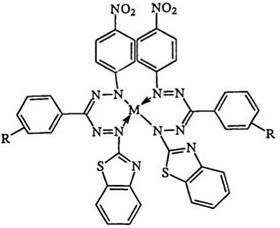
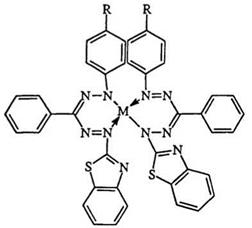
Other transition metals have received much less attention. Complexes of palladium and 2-amino-phenyl-containing formazans have been reported.397 Mercury complexes of tridentate formazans have been studied.398 Silver complexes of tridentate benzothiazolyl-containing formazans have also been studied.399 Recently, alkali and alkaline earth metals have been the subject of many studies. Formazans such as 228 and 229 as well as the macrocyclic 204 have received considerable attention as metal-specific analytical reagents.400-41 1
The synthesis and physical properties of these complexes have received much more attention than structure—property relationships. However,
|
Table 15. Absorption Maxima of Complex 230
(230) |
|
M
|
|
Table 16. Absorption Maxima of Complex 231
(231) |
|
M
|
great interest has been shown regarding the shift in color resulting from complexation.28341 1 — 4 14,416
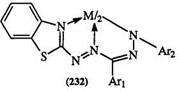
Tables 15 and 16 show the absorption maxima of some metal complexes of benzothiazolyl-substituted formazans 230 and 231.283 The wavelengths are metal ion dependent, making formazans useful reagents for the identification of specific metal ions or the simultaneous determination of two ions. The wavelengths are much longer than those of the formazan anion (Table 14). The general trend for electron-rich substituents is toward a larger shift; this is to be expected as it tends to enhance the aromatic character of the ring and increase the covalent character of the metal — nitrogen bond. The sharpness of the absorption band has been attributed to coordination to the heterocyclic nitrogen as in 232.578
|
|
The IR bands in a number of nickel complexes of triaryl formazans have been assigned by Arnold and Schiele.415 A similar assignment of the electronic bands has been carried out.414 LCAO-MO calculations correlate well with these assignments417 and have been extended to include both inner ligand transitions as well as charge transfer bands and d—d transitions.418 EPR spectra have been used to study the nature of bonding in copper complexes of heterocyclic-containing formazans.419 Metal formazan complexes have also been studied by electrochemistry.283,398,420-422
 7 октября, 2015
7 октября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 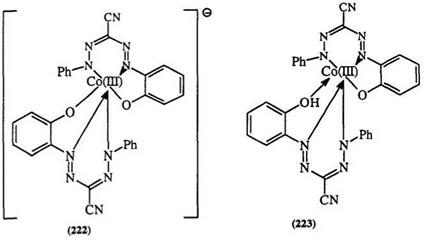
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 