Extensive reviews of synthetic methods and properties of tetrazoles have been published.103,651 — 653
7.З.2.1. From Hydrazoic Acid
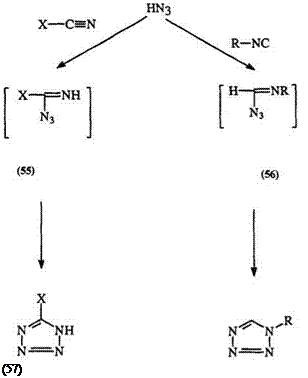
The addition of hydrazoic acid to carbon-nitrogen unsaturated bonds as in hydrogen cyanide, nitriles, and isonitriles leads to unsubstituted, 5-, or
 |
(58)
|
X |
Yield(%) |
Ref |
R |
Yield(%) |
Ref |
|
H |
80 |
105 |
C6H5 |
16 |
124 |
|
z-C3H7 |
87 |
104 |
«-C6H13 |
57 |
125,126 |
|
O-C6H4 |
93 |
106,120 |
(C2H5)2N-C2H4 |
69 |
121 |
|
SCH3 |
71 |
107. 116.118 |
|||
|
N(CH3)-C6H4 |
20 |
113 |
|||
|
N(w-C4H9)2 |
85 |
114 |
|||
|
4-H2N-C6H4 |
10 |
114 |
|||
|
C6H5 |
76 |
106 |
|||
|
4-O2N-C6H4 |
97 |
106 |
|||
|
nh2 |
quant |
105,115 |
|||
|
CO2C2H5 |
— |
114 |
|
Scheme 6 |
1-substituted tetrazoles 57 or 58, respectively, through the unstable imide — azide intermediates 55 and 56 (Scheme 6).104,105 In some special cases, a 1,3-dipolar addition (59) is proposed.32,472 The reaction is usually conduc-
8+ 8_
R—C^=N
® © ©
CC2H5)3N—H—NS^N
‘ (59) —
ted in a sealed tube and is very slow. The use of ammonium azide in dimethylformamide not only avoids the use of the hazardous hydrazoic acid but also accelerates the reaction.106,107,654 Tributyltin azide and trimethyl- silylazide in combination with trimethyl aluminum have been reported as safe sources of hydrazoic acid.108-111 Substituted nitriles such as cyanofor — mates, cyanamides, cyanates, and thiocyanates lead to 5-alkoxycarbonyl and alkyl or arylamino, 5-alkyl or aryl ethers, and thioether derivatives, respectively.106,109,1 12-1 14 5-Amino tetrazole has been prepared from dicyandiamide which acts as a source of cyanamide.115 It is assumed that the cyanamides react as the tautomeric carbodiimides. Using bisisonitriles or dinitriles, this reaction leads to nitrogen — or carbon-linked ditetrazoles 60 and 61, respectively.106,124,125 The intramolecular addition of organic azido
|
(60) (61) X=(CH2)n n= 1-8 |
nitriles, e. g., 62 and 64, can lead to 1,5-fused ring tetrazoles, e. g., 63 and 65 (Eq. 12a, b).116 Though many bistetrazoles and fused ring tetrazoles are important therapeutic agents, there are no reports of their conversion to the corresponding tetrazolium salts.
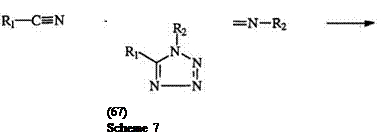
Nitrilium salts, e. g., 66, prepared from the alkylation of nitriles, react with sodium azide to yield 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles, e. g., 67 (Scheme 7).121 The Schmidt reaction,122 a versatile method for the preparation of 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles from ketones and hydrazoic acid, can now be regarded as a special case of azide addition to nitrilium salts.123
![]()
|
 |
Isocyanates132 react with appropriate azide salts to yield 1-substituted tetrazoline-5-ones (68) (Eq. 13). By contrast, isothiocyanatesm. m react with hydrazoic acid to yield the aminothiatriazole (69) which rearranges to the thione under mild alkaline conditions (Scheme 8). Ugi and co — worker126,127 found that when the reaction of isonitriles and hydrazoic
R = Alkyl or Aryl
![]()
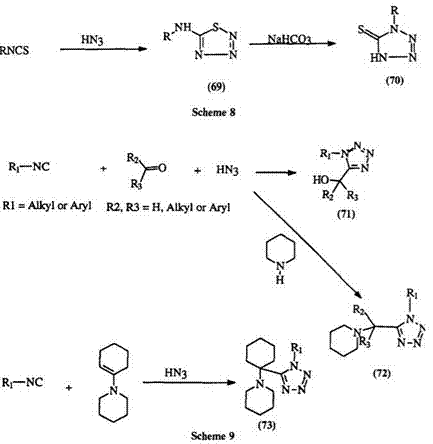 |
acid is carried out in the presence of an aldehyde or ketone, 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles (71) are obtained. A similar reaction occurs when acyl hydrazones or azines are used in place of the ketone or aldehyde.127 The addition of a secondary amine128 to the reaction mixture, or the direct reaction with an enamine in place of the ketone or aldehyde,128 leads to amino-substituted
![]()
|

R = Alkyl or Aryl
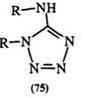
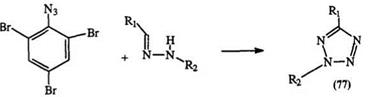
tetrazoles, e. g., 72 and 73, in near-quantitative yields (Scheme 9).128 — 131 1,5-Disubstituted tetrazoles with a nitrogen substituent in the 5-position (75) can be obtained from the reaction of carbodiimides (74) and hydrazoic acid (Eq. 14).135 — 138 Aryl azides, particularly hindered ones, e. g., 76, react with aldehyde hydrazones to yield 2,5-disubstituted tetrazoles (77) in moderate (25—75%) yields (Eq. 15).39.139.140
|
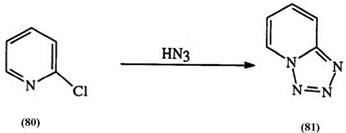
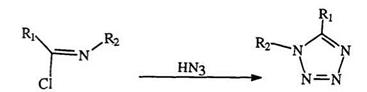
Besides addition reactions, azides or hydrazoic acid can also yield tetrazoles through displacement reactions. Thus, halide displacement in imide chloride (78) yields 1,5-disubstituted tetrazoles (79), and in 2-chloro- pyridine (80), yields tetrazolopyridine (81) (Eq. 16a, b).141 -143 Vinylogous
|
R1, R2 = Alkyl or Aryl
|
|
|
 |
|||
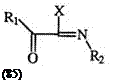
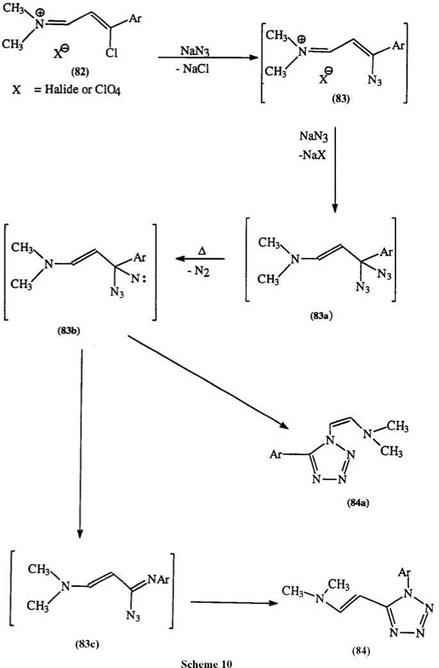
imide chlorides, e. g., 82 react with excess azide to give fair yield (32—70%) of the 5-dimethylamino vinyl derivative (84) through a series of displacements and rearrangements as shown in Scheme 10.144-146 Tr aces of the 1- dimethylamino isomer arising from a vinyl migration, are also isolated. C-acylimide halides (85), which are readily generated from the reaction of acyl halides and isonitriles, yield 1-substituted 5-acyl tetrazoles (86).147 Such displacements are not restricted to halides but can be extended to alkoxy, aryloxy, alkyl, and arylthio groups (Scheme 11).148,149 Recently, the reduction of alkylated tetrazolopyridines has received some attention (see Section 7.3.3.2).
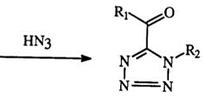 |
Rl, R2 = Alkyl or Aryl X = Halide, O-alkyl, O-aryl, S-alkyl, S-aryl
 15 сентября, 2015
15 сентября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 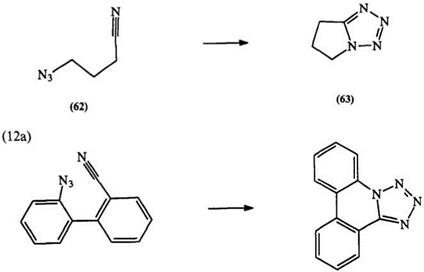
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 