4.4.1. 3,3-Bisheterocyclic Substituted Phthalides
From a commercial viewpoint the most important compounds of this class are the 3,3-(bisindol-3-yl)phthalides. The first synthesis47 involved Route B as described in Scheme 7, in which a second indole derivative condenses with the indolylbenzoylbenzoic acid in acetic anhydride. However, for the preparation of symmetrical derivatives it has been shown61 that a one-pot process, avoiding isolation of the intermediate and use of aluminum chloride, is more convenient.
Bisindolylphthalides such as 13 are red color formers with excellent fastness properties and are used commercially as shading components for the production of black images. Variations on this structure are possible. For example, the introduction of long-chain alkyl groups at the indole nitrogen atoms improves solubility,62 and substitution of the phthalide ring by 5- or 6-dimethylamino groups63 or by four chloride atoms64 results in purple color formers.
Reaction of the indolylbenzoylbenzoic acid with electron-rich heterocycles other than indoles has also produced a number of novel color
|
|
|
(14) |
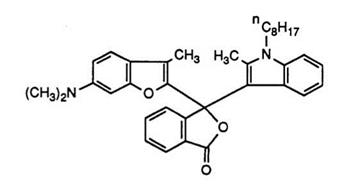
formers. Thus, carbazoles63’64 have been condensed to yield purple color formers, while indolizines65 result in purple to blue images. A vast number of other bridgehead nitrogen-containing heterocycles such as imidazo- [2,1-b]thiazoles have also been condensed66 leading to color formers producing red to blue images, while 6-dimethylamino-2-methylbenzofuran results in 14, a green color former.67
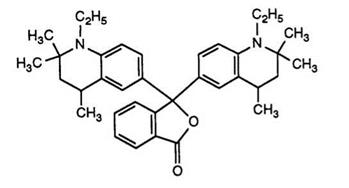
Finally, a number of heterocycles such as quinolines, indoles, and diazines in which the heterocyclic ring is hydrogenated have been reacted as shown in Scheme 7 to produce a number of green color formers such as 15.68
|
|
 2 августа, 2015
2 августа, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 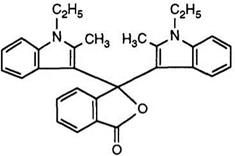
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 