Epoxy resins have only been available commercially since the Second World War and are traditionally based upon the reaction of epichlorohydrin on bis-phenol A, to give a liquid compound of
|
Glycidyl Ether Ether Hydroxyl Ether Ether Glycidyl group bond bond group bond bond group
Epoxy Bisphenol “A” Bisphenol “A” Epoxy group group group group Fig. 2.1. Chemical structure of DGEBA (Ref. 2). |
linear molecules terminating with epoxy groups and having secondary hydroxyl groups occurring at regular intervals. The formal representation of the chemical structure of the resulting diglycidyl ether of bisphenol A (DGEBA) is shown in Fig. 2.1(2). Thus, epoxy resins can be regarded as compounds which normally contain more than one epoxy group per molecule. A general categorisation of the base resins which may be encountered in epoxy adhesive formulations is given in Table 2.2(2) and, of these, the DGEBA and DGEBF resins, or blends of the two, are the types most commonly encountered in two-part room temperature cure epoxy adhesives used in the construction industry.
Adhesive properties of epoxies are obtained by polymerisation using a cross-linking agent, commonly referred to as the hardener,
Table 2.2. A general categorization of epoxy resins (Ref. 2)
Glycidyl epoxy resins Non-glycidyl epoxy resins
I I
Cycloaliphatic Epoxidised olefin resins resins
Glycidyl esters Glycidyl ethers Glycidylamines
1
Glycidyl ethers of Glycidyl ethers of
polyhydric phenols aliphatic polyols
Diglycidyl ether Diglycidyl ether Epoxy novolacs Others of bisphenol ‘A’ of bisphenol ‘F’
—I———-
Blends
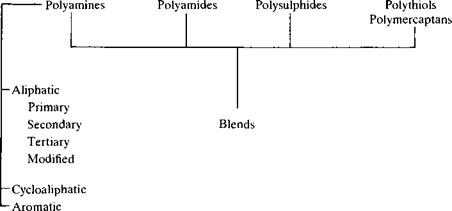 Dicyandiamides Acid
Dicyandiamides Acid
Anhydrides
to form tough three-dimensional polymer networks. A general categorisation of the common hardeners is given in Table 2.3(2) and their general effect on adhesive properties will now be discussed.
 3 июля, 2015
3 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 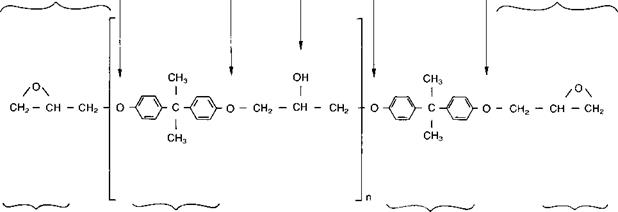
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 