Today, electronic devices are becoming smaller and smaller, their performance is becoming higher and higher, and the mounting density levels in electronic components are growing. Hence, effective solutions for the dissipation of thermal energy are vital. Heat sinks, heat spreaders and other cooling devices are frequently bonded directly to the electronic board to achieve a heat management which is as effective as possible. To this end, the adhesives must not only fulfill the usual demands, for example with regard to a fast and clean processing, but also meet the following requirements:
• good thermal conductivity to provide for a heat transfer between the components
• good dielectric strength to avoid undesired current flows or short circuits
• good vibration damping
• excellent gap-filling features to avoid entrapping of air and to provide for optimal heat transfer
|
Figure 8.58 Bonding of heat sinks to active components. |
• good relaxation behavior to compensate for stress generated by different thermal expansions
• low shrinkage
Thermally conductive products are available as adhesive films, elastomer pads and adhesives. They frequently contain thermally conductive, ceramics-based fillers that substantially improve the heat dissipation from electronic components and, at the same time, have an electrically insulating effect. In addition, they level out any possible irregularities of the surface and have a good initial tack and final bond strength to provide for a correct fastening of the components.
Today, thermally conductive adhesive films (Figure 8.58) have partly replaced thermal conductivity pastes, eliminating the need for mechanical fasteners such as clamps or screws. They are capable of leveling out any possible irregularities of up to 20% of their own thickness. A typical application is the bonding of heat sinks to computer central processing units and to flexible or rigid circuit boards. Thick adhesive films are also suited for heat dissipation in modern plasma panels. Weakly adhering, thermally conductive elastomer pads have special gap-bridging properties capable of leveling out differences of up to 2.5 mm, although additional mechanical fasteners are required. Thermally conductive adhesives combine low thermal impedance with high mechanical strength, and also have excellent wetting and gap-filling properties.
8.7.2
 21 декабря, 2015
21 декабря, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 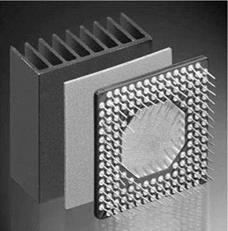
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 