Both, aromatic and aliphatic isocyanates, are used for the synthesis of polyurethanes. The most popular aromatic isocyanates are 2,4-toluene diisocyanate (TDI; an isomeric mixture of 2,4- and 2,6-toluene diisocyanate at an isomer ratio of 80 : 20 or 65 : 35), 4,4-methylene dip(henyl isocyanate) (MDI), and the oligomeric form of MDI, a phosgenized aniline formaldehyde condensate. The most commonly used aliphatic and cycloaliphatic diisocyanates are hexamethylene diisocyanate, isophorone diisocyanate, 2,2,4-trimethyl hexamethylene diisocyanate, and 2,4,4-trimethyl-hexamethylene
|
Figure 5.21 Commercialized aromatic and aliphatic diisocyanates. (a) TDI; (b) MDI: (c) oligomeric MDI; (d) hexamethylene diisocyanate; (e) 2,2,4-trimethyl hexamethylene diisocyanate; (f) 2,4,4-trimethyl hexamethylene diisocyanate. |
diisocyanate. Some structures of diisocyanates are shown in Figure 5.21. For the manufacture of polyurethanes, aromatic diisocyanates are preferred to their (cyclo) aliphatic counterparts because they are less expensive and more UV-stable.
 13 сентября, 2015
13 сентября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 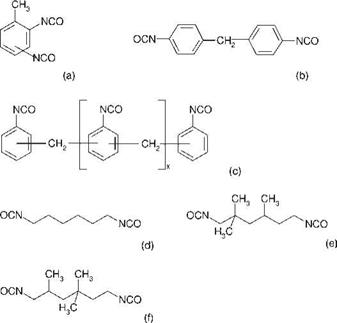
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 