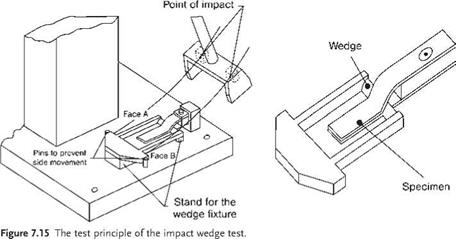
In some cases adhesive joints are required to maintain the structural integrity of bonded parts even under high dynamic loading conditions, for example in a car body during a crash situation. ISO 11343 [4] describes a procedure for the ‘Determination of dynamic resistance to cleavage of high strength adhesive bonds under impact conditions — Wedge impact method’, while ISO 9653 relates to a ‘Test method for shear impact strength of adhesive bonds’. According to the standard, ISO 9653 determines the average cleavage resistance, expressed as force or energy, of a structurally bonded metal joint. The cleavage corresponds to the separation of the adherents by a wedge, moving at high speed, the displacement of which is initiated by the impact of, for example, a pendulum hammer (Figure 7.15).
In practice, tests with application-specific parts and geometries are necessary to assess the impact resistance of a bonded structure. Since, for example, automotive crash tests are cost-intensive significant effort has been applied to seek ways in which to simulate and predict crash performance by using numerical tools such as finite element simulation.
|
Figure 7.14 Time-dependent stress-strain behavior in creep and relaxation experiments. |
|
|
7.3.3
 19 октября, 2015
19 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 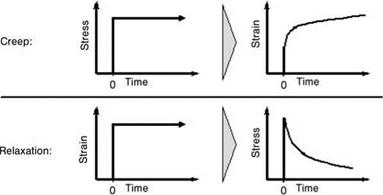
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 