Bonding is the most important method of closing packages made from paper, cardboard or paperboard. Depending on the automation level of the packaging line, the design of the machinery and the demands placed on the packages during transport and storage, one of the following systems is used:
• hot melts
• PSA packaging tapes
• water-activated adhesive strips
On occasion, dispersion adhesives are also used, particularly with the two-shot method (i. e. in combination with hot-melt adhesives). This combination is used, for example, when a rapid setting process is required by the production machinery (hot melts), and a good thermal and chemical resistance, for example to essential oils, is also needed for safe and durable bonding (dispersion adhesives).
|
|
|
Figure 8.28 Carton closure. |
Hot Melts The hot-melt adhesives used in the packaging sector are thermoplastic water-insoluble polymer mixtures (see also Section 5.2). For carton closure purposes (Figure 8.28), mainly EVA copolymer-based products are used, but the new polyolefin — based adhesives are also becoming popular for carton closing as well as for tray set-up.
For special applications (e. g. hot filling), copolyamide — or copolyester-based hot melts, with substantially higher melting ranges, are chosen. The adhesives can be tailored to meet the needs of a desired application by mixing them with resins (hydrocarbon resins or natural resin derivatives), waxes or other polymers. The hot melts are solid at room temperature, are applied in the molten state (Figure 8.29), and set within the subsecond time range.
The adhesive films formed when carton flaps are joined have a thickness of approximately 0.2-0.8 mm. It is possible to obtain high speeds of machinery by using hot melts, but such applications require the correct equipment with an appropriate initial investment expense. This disadvantage is outweighed, however, by a good running performance on the machinery, the result being production lines that run more efficiently. In recent years the development of low-temperature hot melts has
|
|
|
266 I 8 Adhesive Bonding Technology: Fields of Application Temperature (°С) |
|
140 °С 120 °С 100 °С 80 °C — 60 °C- 40 °C — 20 °С |
|
Figure 8.30 Application temperatures for conventional and low-temperature hot melts. |
become increasingly popular [30]. Compared to conventional products, which were processed at operating temperatures between 160 °C and 180 °C, low-temperature hot melts can be processed at substantially lower temperatures ranging between 120 °C and 140 °C (Figure 8.30).
Owing to lower application temperatures, these hot melts are subjected to considerably lower thermal stress, which results in an improved viscosity and color stability. Because the application equipment is also exposed to lower temperatures, it has a longer service life and requires less maintenance and energy input.
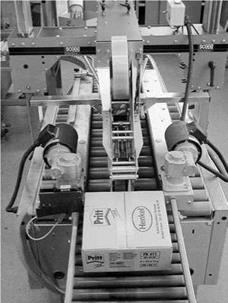
PSA Packaging Tapes These tapes are used for the closing of cartons (Figure 8.31) and have a width of a few centimeters (preferably 30-100 mm). They are coated with a PSA, which means that at room temperature they adhere to a surface upon application of pressure (see Section 5.1). Biaxially oriented polypropylene film (BOPP) is the most frequently employed base material in the packaging sector (ca. 80%). PSA tapes with PVC as the base material are only rarely used, and in some exceptional cases paper is accepted as the base material. Today, the following three systems are in common use for the manufacture of PSA tapes: solvent-based PSAs (ca. 45%); waterborne dispersion systems (ca. 25%); and hot melts (ca. 30%), which are becoming more popular. The adhesive film thickness on the base material is generally 16-25 pm.
Water-Activated Adhesives Water-activated adhesive tapes or strips are commonly made from high-strength (50-150 gm-2) kraft paper coated with a water-activated (usually nonthermoplastic) adhesive (e. g. animal or plant glue). The strips are sometimes reinforced with filament yarn to increase their tensile strength. Before application of the tape, the gumming adhesive is reactivated with water that penetrates into the carton, resulting in the setting of the adhesive.
Reclosure Systems for Liquid Packaging Boards Consumer-friendly closure systems are an integral part of up-to-date liquid-packaging boards (also called ‘fitments’), as
|
Figure 8.31 Closing of cartons by means of PSA tapes. |
their convenience adds customer-appeal to many packages. These devices are expected to allow easy and clean opening (without auxiliary aids such as scissors or knives), pouring and hygienic reclosure; evidence of tampering is often also required. There are two reclosure options: (i) screw caps that provide for a reliable reclosure and horizontal storage; and (ii) snap closure systems. These are usually made from polypropylene and are safely and economically applied by means of hot melts. As liquid packaging boards usually have a polyolefin cover, only special hot melts can be used for this purpose. Polyolefin copolymer-based hot melts, for example, have a sufficiently large adhesion spectrum that enables them to bond reliably to the relatively nonpolar polyolefins. Adhesives are applied to the spouts by means of rollers or special nozzles, and have an adhesive film thickness of up to 0.5 mm [31].
As many beverages are stored in a refrigerator, the bonds must resist low temperatures. Usually, bonding stability at storage temperatures between 3 °C and 50 °C must be guaranteed.
8.5.4
 29 ноября, 2015
29 ноября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 


 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 