Addition silicones for bonding and sealing purposes were developed later than condensation silicones. These modern systems consist of a siloxane with a terminal vinyl group, and a siloxane with a hydrogen atom that is directly bound to the silicon.
The exothermic addition reaction is platinum-catalyzed (Figure 5.36) and, when conducted at room temperature, full cure is generally obtained within 24 h. The reaction is significantly accelerated by an increase in temperature; raising the temperature to 150 °C leads to a full cure within 10 min. Special formulations, containing inhibitors, are stable at room temperature and cure at higher temperatures.
|
Figure 5.36 Polyaddition of a two-part silicone system. |
88 I 5 Chemistry and Properties of Adhesives and Primers
 27 сентября, 2015
27 сентября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 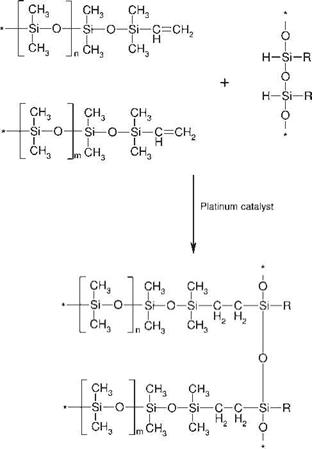
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 