Tests to establish shear strengths and percent material failures for adhesively bonded wood-wood and FRP-wood interfaces were performed using a modified ASTM D905
![]()
 |
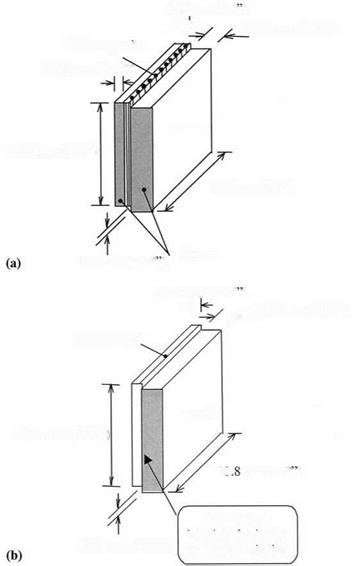 6.35 mm (0.25")
6.35 mm (0.25")
Figure 5 Modified ASTM D905 specimens for block-shear test. (a) Phenolic FRP-wood specimen; (b) epoxy FRP-wood specimen.
tested following the ASTM D905 standard. Initially, all the block-shear samples were conditioned to wood equilibrium moisture content of 12% in an environmentally controlled chamber. To obtain the wet condition, half of the block-shear wood-wood and FRP-wood samples were subjected to a vacuum-pressure soak cycle. The samples were placed in a container and submerged in water, and the container was then placed in a cylinder that was equipped to apply vacuum and pressure. A vacuum of 0.635 m (25 in) Hg was applied for 40 min, followed by a pressure of 0.690 MPa (100 psi) for another 40 min. This vacuum — pressure soak cycle was satisfactory for impregnating the wood layers with water [10]. The increase in moisture content by weight was more than 100% at the end of this cycle. The vacuum-pressure soaked wood-wood and FRP-wood block-shear specimens were immediately tested wet for shear strength according to the ASTM D905 standard. All the block-shear specimens were tested on a universal testing machine, and the loading rate (displacement controlled mode) of 0.381 mm/min (0.015 in/min) specified by the test standard was used.
 14 июля, 2015
14 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 