Formazans are stable in alkaline solution. Alkaline hydrolysis of functionalities on formazans such as nitriles, esters, and amides leads to the acids (Section 1.3.1.1). The case of 3-nitroformazans (198) is unique. Reaction with hydroxide ion gives 3-hydroxy formazan (199) which can be readily oxidized to the tetrazolium betaine. In the presence of hydrosulfide, a reduction of the nitro group takes place giving 3-aminoformazan (200) with traces of the 3-mercaptoformazan (201), which by contrast is the main product when ammonium polysulfide is used (Scheme 30).45,346
|
Scheme 30
 3 октября, 2015
3 октября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 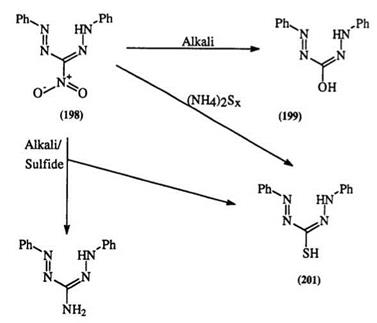
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 