6.4.1.2. Background
Thermosensitive recording paper was introduced by the National Cash Register Company in 1968. The chemistry employed is essentially the same as that for carbonless papers, i. e., color-formation reaction between leuco dye and coreactant, though thermosensitive recording papers require certain unique leuco dyes and coreactants. Thermosensitive recording papers generally consist of a single-sheet system in contrast with the two-sheet system for carbonless copying papers. The surface of the sheet has a thermosensitive layer comprising leuco dye and coreactant as essential color-forming components together with several additives. A cross-sectional view of the structure is shown in Figure 6.8.
The thermosensitive recording paper itself is white like a plain sheet of paper. With the application of heat by means of a thermal pen or thermal head, the color-forming components in the thermosensitive layer are brought into reactive contact in the area delineated by the heat pattern resulting in a distinct image.
The color-forming mechanism is simple and direct, only requiring heat application, and the recording equipment is free from maintenance, highly reliable, and less expensive. Thermosensitive recording papers can be used
|
^Thermal head q Colored image s’ |
Leuco dye Co-reactant |
|
— Thermo-sensitive layer |
|
|
Figure 6.8. Structure of thermosensitive recording paper. |
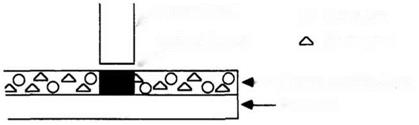
Substrate
for various purposes. These include facsimile, medical instruments such as electrocardiograph, spectrophotometer, printer, and video printer. Today, the demand of thermosensitive recording paper for facsimile is 70% or more in total consumption of 300,000 tons worldwide.
 10 сентября, 2015
10 сентября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 