The reaction of the keto acids (66) with 4-alkoxydiphenylamines (75; R = CH3, C2H5) is widely used to prepare fluoran compounds developing green or black colors. The reaction in concentrated sulfuric acid gives intermediate phthalide compounds (76), which are then treated with base to convert into 2′-anilino-6′-aminofluorans (77) (Eq. 5).
|
|
It is essential that the temperature of the first step not exceed 35 °C to minimize undesirable decomposition of the 4-alkoxydiphenylamines. In addition, the 4-alkoxydiphenylamines should be added to a solution of the keto acids in sulfuric acid. The reverse order of addition does not produce good results, because the 4-alkoxydiphenylamines are liable to decompose in sulfuric acid even at lower temperature. On the other hand, the phthalides are stable to a considerable extent in sulfuric acid at 35°C or below. The reaction is substantially completed in a few hours after dissolution of the 4-alkoxydiphenylamines. The second step proceeds easily at 50 °C or higher, and sodium hydroxide is successfully employed as base, though any base can be used.
The reaction of the keto acids with 4-hydroxydiphenylamines (75; R = H) gives directly the fluoran compounds (77), not via phthalide intermediate. The yields, however, are much lower than those using 4- alkox ydiphen ylamines.
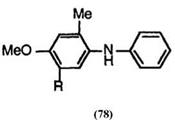
In addition, the reaction with 4-methoxydiphenylamines having a f-butyl group on the anisole moiety does not give the corresponding fluoran compounds, because the f-butyl group is liable to eliminate in sulfuric acid. For example, the reaction of 5-f-butyl-4-methoxy-2-methyldiphenylamine (78; R = f-C4H9) with keto acid gives the same product derived from 4-methoxy-2-methyldiphenylamine (78; R = H).
|
|
Table 6 shows melting points of various 2′-anilino-6′-aminofluorans (77).
Some fluoran compounds in Table 6 are found to form adducts with solvent. For example, when 6′-diethylamino-2′-(2,4-dimethylanilino)-3′- methylfluoran (77e) is recrystallized from toluene, it forms an adduct, mp 137-139°C, having 0.5mol of toluene of crystallization per mol of the fluoran; the toluene of crystallization liberates on treatment with boiling n-hexane or isopropanol or on heating in vacuo. 2′-Anilino-6′-(N-cyclo- hexyl-N-methylamino)-3′-methylfluoran (77c) forms an adduct with acetone69 having a melting point of 133-135 °C. 2′-Anilino-6′-(N-ethyl-N — isobutylamino)-3 ‘-methylfluoran (77g) forms adducts with acetone69 and 2-butanone69 having a melting point of 139-141 and 128-129 °C, respectively. 2′-Anilino-6′-(N-ethy1-4-methy1ani1ino)-3’-methylfluoran (75) also forms an adduct with acetone69 having a melting point of 152-153 °C.
Preparation of 2′-Anilino-6′-diethylamino-3′-methylfluoran (77d). To a solution of 2-(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzoic acid (0.1 mol) in 98% sulfuric acid (1 50 g) was added 4-methoxy-2-methyldiphenylamine (0.1 mol) in limited amounts, while the temperature was maintained to not rise above 30 °C. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 20 h, and poured into ice water (1000 ml). The precipitate was filtered off, washed with water, and then refluxed with a mixture of toluene (400 ml) and 20% aqueous sodium hydroxide (150 g) for 1 h. The toluene layer was separated, washed with hot water, and concentrated to leave ca. 100ml of toluene. The residue was then refluxed with methanol (100 ml) for 1 h. After being cooled, the precipitate is filtered off, washed with methanol, and dried to give 2′-anilino-6′-diethylamino-3′-methylfluoran in 90% yield as an off — white powder, mp 197-198 °C.
Preparation of 6′-Diethylamino-2 ‘-(2,4-dimethylanilino)-3 ‘-methylfluoran (77e). To a solution of 2-(4-diethylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzoic acid (0.1 mol) in 98% sulfuric acid (150 g) was added 4-methoxy-2,2′,4’- trimethyldiphenylamine (0.1 mol) in limited amounts, while the temperature
|
77 |
R1 |
R2 |
R3 |
R4 |
R5 |
О 0 % |
|
a |
CH3 |
CH3 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
202-203 |
|
b |
CH3 |
n-C3H7 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
175-178 |
|
c |
CH3 |
C-C6H11 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
206-208 |
|
d |
CH5 |
C2H5 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
197-198 |
|
e |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
CH3 |
H |
2,4-(CH3)2 |
170-172 |
|
f |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
CH3 |
H |
2,6-(CH3)2 |
163-164 |
|
g |
C2H5 |
i-C4H9 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
151-154 |
|
h |
C2H5 |
i-C5H11 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
164-167 |
|
i |
C2H5 |
C2H5OC3H6 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
151-153 |
|
j |
C2H5 |
4-CH3 C6 H4 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
207-209 |
|
k |
n-C4H9 |
n-C4 H9 |
CH3 |
H |
H |
180-182 |
|
l |
— (CH2)4— |
CH3 |
H |
H |
216-218 |
|
|
m |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
CH3O |
H |
H |
174-175 |
|
n |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
Cl |
H |
H |
179-180 |
|
o |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
H |
2-Cl |
221-223 |
|
p |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
H |
3-CF3 |
180-181 |
|
q |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
H |
4-CH3 |
212-216 |
|
r |
n-C4H9 |
n-C4 H9 |
H |
H |
2-Cl |
185-188 |
|
s |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
CH3 |
H |
158-160 |
|
t |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
CH3 |
3-CF3 |
146-148 |
|
u |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
CH3 |
4-CH3 |
171-172 |
|
v |
C2H5 |
C2H5 |
H |
C2H5 |
H |
142-143 |
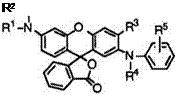 |
was maintained to not rise above 30°C. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 20h, and poured into ice water (1000ml). The precipitate was filtered off, washed with water, and then refluxed with a mixture of toluene (400 ml) and 20% aqueous sodium hydroxide (150 g) for 1 h. The toluene layer was separated, washed with hot water, and concentrated to leave ca. 100 mL of toluene. After being cooled, the precipitate was filtered off, and dried to give an adduct with toluene. The adduct was then refluxed with isopropanol (100 ml) for 1 h. After being cooled, the solid was filtered off, and dried to give 6′-diethylamino-2′-(2,4-dimethylanilino)-3′- methylfluoran in 83% yield as an off-white powder, mp 170-172 °C.
Preparation of 2′-Anilino-6′-di-n-butylamino-3′-methylfluoran (77k). To a solution of 2-(4-di-n-butylamino-2-hydroxybenzoyl)benzoic acid (0.1 mol) in 98% sulfuric acid (150 g) was added 4-methoxy-2-methyl — diphenylamine (0.1 mol) in limited amounts, while the temperature was maintained to not rise above 30°C. The resulting mixture was stirred at room temperature for 20h, and poured into ice water (1000ml). The precipitate was filtered off, washed with water, and then refluxed with a mixture of toluene (400 ml) and 20% aqueous sodium hydroxide (150 g) for 1 h. The toluene layer was separated, washed with hot water, and concentrated to leave ca. 100 ml of toluene. After being cooled, the precipitate was filtered off, and dried to give 2′-anilino-6′-di-n-butylamino-3′-methylfluoran in 90% yield as a white powder, mp 180-182°C.
 1 сентября, 2015
1 сентября, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 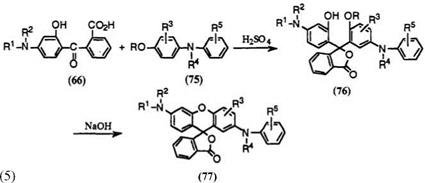
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 