Applications of photochromic materials take advantage of a specific color change, and are found especially in the field of decorations, such as textiles and paints.1,2 The systems that utilize reverse coloration of photochromic compound are sunglasses, car windows, windowpane, information storage, and display media. Light sensitivity of photochromic materials is much lower than that of silver halides. However, they have sufficient sensitivity to laser light and UV light sources. Although spiroben — zopyran is not useful for practical applications, spirooxazine and spiroben — zothiopyran are practically useful for sunglasses and optical data storage, respectively.
Polymers containing photochromic compound, such as spiroin-
dolinobenzopyran, have much more practical use than simple monomeric compounds. In the polymer matrix, the equilibrium between spiropyran and photomerocyanine forms depends on the temperature and polymer matrix, and the glass transition temperature.35 However, when photochromic polymer, e. g., containing spirobenzopyran, is irradiated by UV light at high temperature, it may no longer exhibit color, since under these conditions, photocoloration and thermal fading reaction may be competitive.
The photochromisms of spiroindolinobenzopyrans trapped in glass prepared by the sol-gel method have been stuied.36,37
For thermographic recording materials, thermochromic properties of the spiroindolino — and spirobenzothiazolino-benzopyrans have been utilized. As an example, thermal paper patented by National Cash Register38 can be cited. In this paper, the colored merocyanine form is fixed by reacting with phenols or metallic salts.2
Solid films of spiropyrans are important in optical data storage. Thin films of spirobenzopyran (1.0 pm) have been prepared by vacuum deposition, and its reversible photochromism has been confirmed.39 The J-aggre-
 |
Scheme 8
gation form of photomerocyanine in Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) film is attempted in multioptical data storage using at least two laser.46,47
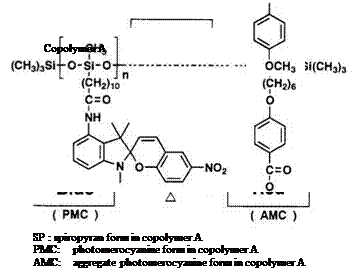
Photochromic materials with liquid-crystal polymer40-42 are interesting advanced materials, due to their sensitivity to light, electric, and magnetic fields. Copolymers of polyacrylic or polysiloxane backbone, con-
taining a high percentage of spirobenzopyran and a mesogenic group, have been prepared. In such compositions, aggregation of the colored form with stacklike structure is formed.43-45 For example, when the yellow film of polymer A is irradiated with UV light below —20°C, the blue colored form (580 nm), i. e., normal photomerocyanine form, is produced. Heating the blue film to 25°C produced red coloration (Scheme 8).42 This colored form is the H-aggregated polymer of photomerocyanine, in which the molecular dipole is antiparallel, absorbing at ^max 550 nm. The yellow form can be reversed from the red or blue form with visible light. Thus, basic three color forms from copolymer A can be produced by reversible reaction, as shown in Scheme 8.
 24 июня, 2015
24 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 