Hydroxy functional acrylics will cure with all types of amino resins, including urea formaldehyde, melamine formaldehyde (MF) and benzoguanamine formaldehyde types. Urea formaldehyde resins are faster curing and cheaper than the other two main types, but they are rarely used with acrylics due to inferior film performance (e. g. resistance properties and exterior durability).
Benzoguanamine based amino resins are not widely used with acrylics due to their inferior flow and compatibility. These characteristics, combined with their cost, make them unattractive crosslinking resins for acrylics.
The most common amino resins used with acrylics are those based on melamine, see Figure 4-6.
5HCHO
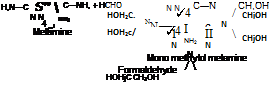 |
I
Hexa methylol melamine
Figure 4-6
Melamine Formaldehyde Resins
Melamine is reacted with formaldehyde to produce up to 6 methylol groups per melamine molecule.
An increase in molecular weight is achieved through condensation of the methylol groups. This is followed by etherification with butanol, which improves the solubility and compatibility with acrylic resins, see Figure 4-7.
|
H |
HOH, C |
. N |
H |
|
/ |
2 |
S |
/ |
|
c—N |
N’ |
—c c— |
N |
|
H N CH2OH |
+ X |
I II N N |
4 CH2OH |
|
HOH’C ,N4 |
|
c’ I NH, |
The properties of the resultant butylated MF resin are governed by the methylol content, degree of butylation and molecular weight as shown in Table 4-1®’
|
TABLE 4-1: EFFECT OF COMPOSITION ON PROPERTIES
+ Increase — Decrease |
 11 августа, 2015
11 августа, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 