In the steady state the rate of formation of radicals by initiation, is equal to the rate of removal of radicals by termination.
That is:
кгі [~Мг][Мі] = k-|2 [~Мі][Мг] equation A The rate of consumption of monomer M! is given by
= ki, i [- МІ] [Mi] + кг, і [~ М2] [Mi] equation В
The rate of consumption of monomer M2 is given by
From equation A
Substituting for [~Mi] in equations В and C
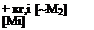
-d [Mi] = ki, i кг,1 [~Мг] [Mi]2 dt Ki,2 [М2]
and
![]() Ki,2 Ка,1 [-M2] [Mi] [M2] + K2,2 [~M2] [М2]
Ki,2 Ка,1 [-M2] [Mi] [M2] + K2,2 [~M2] [М2]
Kl,2 [М2]
™jjT^ = [~M2](k2,l[Ml] + k2,2[M2])
then
d [Mi] d[M2]
By replacing t-^1 with r, к,2
and ~ with r2 *2,1
the following equation is obtained
d [Mi] = [Mr] ( n [Mi] + [M2]) d [M2] [M2] ([Mi] + r2 [M2])
where: r, represents the reactivity of Mi with respect to Mi and М2
r2 represents the reactivity of М2 with respect to М2 and Mi.
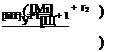 |
||
The equation is known as the copolymer composition equation.
The copolymer equation is normally used in this form to predict, by calculation, the composition of a polymer resulting from the polymerisation of two monomers.
 27 июня, 2015
27 июня, 2015  Malyar
Malyar  Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 