Typical application areas for UV adhesives in the medical industry include the assembly of blood collection devices, endoscopes, hearing aids, IV sets, infusion pimps, catheters and diagnostic imaging equipment. The UV adhesive is often used to bond a stainless steel guide wire inside a polycarbonate luer or similar moulded part.
Other applications include cannula/hub bonding, blood filters, tracheal tubes, colostomy bags and appliances, cuff and tube assemblies and inflators.
Most of these devices are single-use and so will be sterilised by gamma radiation or by EtO and this will not usually affect the performance of UV adhesives. Some grades of UV adhesives will withstand repeated autoclave cycling (steam at 135 °C) but many grades will deteriorate after a number of cycles and so tests should always be conducted.
|
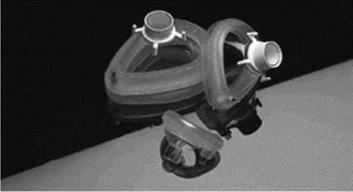
Figure 9.6 Bonding tracheotomy cuffs [5] |
Figure 9.6 shows the bonding of tracheotomy cuffs and balloon catheters. In both applications the UV adhesive allows the parts to be correctly positioned prior to curing. UV adhesives are more flexible than cyanoacrylate adhesives and are therefore well suited to applications where some flexibility is required.
For applications where a high degree of flexibility is required and where repeated autoclaving may be necessary, the UV-curing silicone products are used (Figure 9.7). These products are immobilised with UV light and then continue to fully cure by absorbing moisture from the atmosphere. The products are also referred to as UV-curing room-temperature-vulcanising silicones.
|
|
Without UV, the products will skin over in about 10-15 minutes but will cure to a depth of up to 6 mm in 72 hours. The cure process is characterised by the release of by-product, which often carries a distinctive odour (e. g., vinegar). Neutral cure versions (alkoxy silicones) are also available.
 31 декабря, 2015
31 декабря, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 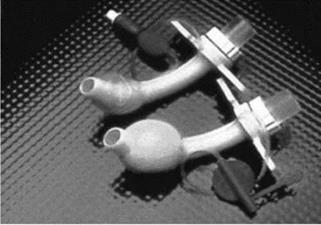
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 