Since ca. 1935, and especially in Mediterranean countries, blue inorganic fungicides based on copper and mostly used for treating vines, olives or citrus fruits have largely been replaced by colorless organic compounds. Micronized iron blue pigments are used to color these fungicides (normally at a concentration of 3-6 wt.%), so that even small amounts become visible due to the high color intensity, and precise control is possible. The fungicide is usually milled or mixed with a micronized iron blue pigment [3.187].
A welcome side effect of treating fungi (e. g. peronospora plasmopara viticola) with iron blue is the fertilizing of vines in soils that give rise to chlorosis. Leaf color is intensified, ageing of the leaves is retarded, and wood quality (“ripeness”) is also
|
Fig. 3.25 Color locations of black offset printing inks with different toning. ■ 1-4: Pigment Black LCF (= Printex® 35), + 5-7: Pigment Black LCF/Manox® Easisperse®, x 8-10: Pigment Black LCF/[Manox® Easisperse®-Pigment Red 57:1 (4:1)], *11-13: Pigment Black LCF/Pigment Blue 61, A 14-16: Pigment Black LCF/Pigment Blue 15:3. |
![Agriculture Подпись: Fig. 3.26 Stepwise approach to the achromatic point of a Printex® 35 offset printing ink by using Manox® Easisperse® and/or Pigment Blue 61 as toning pigment [3.191].1) Printex® 35, 2) Manox® Easisperse®, 3) Pigment Blue 61,4-6) Printex® 35/Manox® Easisperse®, 7-9) Printex® 35/Pigment Blue 61, 10-11)](/img/1206/image063.png) |
Printex® 35/Manox® Easisperse®/Pigment Blue 61. Points 4 and 7 contain 3% blue pigment; points 5 and 8, 6%; points 6 and 9, 9%. Point 10 results from mixing 2% Manox® Easisperse® and 4% Pigment Blue 61; point 11 by mixing in the ratio 3:3.
improved [3.188-3.190]. Iron is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis, which improves grape quality and yield. Other iron salts do not have this effect [3.189].
3.6.4.3
 27 ноября, 2015
27 ноября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 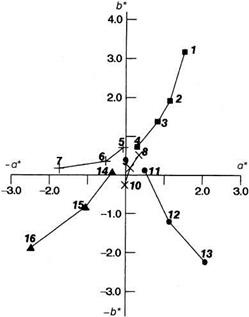
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 