Coumarone indene resins (Figure 2.74) are one important class of hydrocarbon resins. They are mixtures of homopolymers and copolymers of coumarone and indene. Coumarone and indene are obtained together in fractional distillation of coal-tar naphtha. They are polymerized through their unsaturation using either sulfuric acid or metal chloride catalysts. The products are low MW polymers varying from viscous liquids to hard and brittle solids (softening point 90 to 140 °C). They have good compatibility with many of the binders used in coatings and are often used as modifiers to improve gloss and drying time. Due to the absence of acidity, they are good hard binders for aluminum paints and provide good leafing stability. Some low viscosity grades are also used as plasticizers in epoxy coatings.
|
Figure 2.74: Schematic representation of coumarone indene resin |
 30 октября, 2015
30 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 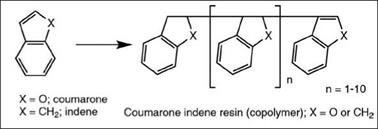
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 