This class of epoxide resins is completely different than the resins discussed so far. Internal epoxy groups (Figure 2.43) have very different reactivity compared to glycidyl epoxy groups. These epoxy resins are typically prepared by epoxidation of carbon double bonds (olefin type) using peracids or hydrogen peroxide. Epoxidized vegetable oils (mainly soybean oil and linseed oil) are important products of this class. Other important resins in this class are cycloaliphatic diepoxy compounds such as 3,4-epoxycyclohexylmethyl-3’,4’-epo — xycyclohexylcarboxylate. The internal epoxy groups have reduced reactivity towards nucleophiles but can easily undergo self-condensation induced by Lewis or Bronsted acids. Therefore they are frequently used in cationically cured thermal or photocured coating systems. They can also be used by cross-linking with polycarboxylic acids and anhydrides.
|
|
 5 октября, 2015
5 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 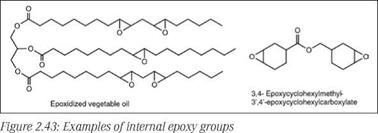
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 