Reactive diluents are low viscosity mono — or difunctional epoxies based on aliphatic alcohols, diols, alkylated phenols or carboxylic acid that are used to reduce the viscosity of standard epoxy resins and react with curatives during the curing process (Figure 2.42). They tend to reduce chemical resistance, heat resistance and hardness of the coatings. The difunctional diluents have fewer negative effects than monofunctional diluents. Higher vapor pressure (volatility) of some of the reactive diluents increases their toxicity, health risks and problems with skin irritancy.
|
|
Glycidyl ethers of polyalkylene glycols are low viscosity epoxy resins that are useful as reactive diluents for conventional BPA epoxy resins. Their aliphatic ether backbone structure improves flexibility, elongation and impact resistance. However, heat, solvent, water, chemical and corrosion resistance are reduced. They are therefore frequently employed as a modifier rather than the sole binder.
 4 октября, 2015
4 октября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 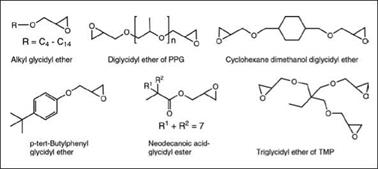
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 