Resoles are produced by a base catalyzed reaction between phenols and formaldehyde with a molar excess of the formaldehyde (f:p > 1), see Figure 2.19. Methylolated phenol is more reactive than phenol; therefore, once the reaction starts, the reaction accelerates in a short time. A higher molar excess of formaldehyde increases the reaction rate but results in a low MW polymer, while lowering the f:p, though still keeping it >1, gives a higher MW product with a lower reaction rate. The methylol group can react at the ortho or para position of another phenol molecule, producing a methylene linkage and thus giving rise to a polymeric structure. Polymerization may also occur by reaction of the hydroxymethyl group of methylolated phenol with the methylol group of the other molecule to form a dimethylether linkage. Upon further heating, these ether linkages get converted to methylene linkages by liberating formaldehyde. Resoles, by virtue of having reactive methylol groups, are thermosetting resins that can self-cross-link upon heating or acid catalysis.
|
Figure 2.19: Synthesis of resole from phenol and formaldehyde |
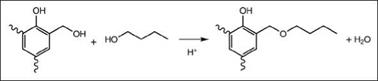
The classical resoles produced from phenol and formaldehyde are viscous brown syrups soluble in alcohol, which are not suitable as the sole film forming agents in coatings because of their poor flexibility. However, they are used as a curing agent for hydroxyl functional resins, such as alkyds and polyesters, imparting flexibility. The more useful products for the coating industry that are storage stable and compatible with other resins are produced by partial or full replacement of phenol with alkyl or aryl substituted phenols. In another approach, methylol functional resoles are etherified with aliphatic alcohols (Figure 2.20). The type of alcohol and level of etherification is varied to tailor reactivity, compatibility and solubility.
|
Figure 2.20: Etherification of resole with aliphatic alcohol |
Resoles are used as cross-linkers for resins such as alkyds, epoxies, epoxy esters or polyesters. Such coatings find applications in drum and can linings, tank linings and pipe coatings. Phenolic resole or epoxy based baking systems, due to their very good chemical resistance at low film thickness, are popular as linings for food and beverage cans.
 19 сентября, 2015
19 сентября, 2015  Pokraskin
Pokraskin 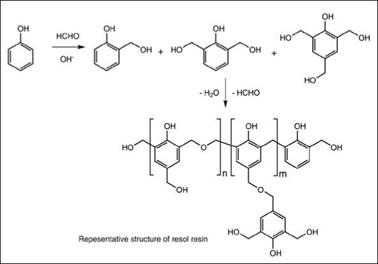
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 