Viscosity is defined as the property which determines the resistance to motion when a sheering force is exerted on the fluid under laminar flow conditions.
If denotes the dynamic viscosity of a polymer solution of concentration C, and i)0is the intrinsic viscosity of the solvent of the same temperature, then:
_ — Лг Ло
where: T|r is the relative viscosity.
Also:
![]() Т1-Л0
Т1-Л0
Л0
where: t|sp is the specific viscosity.
T|s
The ratio of is the reduced viscosity or viscosity number.
![]() [T|] is the intrinsic viscosity
[T|] is the intrinsic viscosity
[T|] is determined experimentally from a plot ofvs c as shown below.
|
Figure 1-63 |
The intrinsic viscosity characterises the capacity of the polymer to increase the viscosity of the system when unaffected by the presence of other polymer molecules, that is at zero concentration ( when C = zero ).
There is no direct method for obtaining molecular weight from the intrinsic viscosity of a polymer.
The Mark-Houwink Equation relates to the molecular weight in a practical way.
fa] = KM“
Where К and a are constants for the particular solvent-polymer system at a given temperature and are determined experimentally.
 1 июля, 2015
1 июля, 2015  Malyar
Malyar 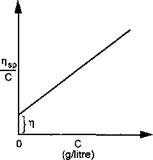
 Опубликовано в рубрике
Опубликовано в рубрике 